NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Page No.172
Question 1:
What does an electric circuit mean?
विद्युत परिपथ का क्या अर्थ है?
Answer
A continuous closed path made of electric components through which an electric current flows is known as an electric circuit.
किसी विद्युत धारा के सतत् तथा बंद पथ को विद्युत परिपथ कहते हैं।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 2:
Define the unit of current.
विद्युत धारा के मात्रक की परिभाषा लिखिए।
Answer
The unit of electric current is the ampere.
One ampere is defined as the flow of one coulomb of electric charge passing through a conductor in one second. It is commonly abbreviated as A.
विद्युत धारा का SI मात्रक ऐम्पियर है।
1 ऐम्पियर विद्युत धारा की प्रवाहित मात्रा है, जो 1 कूलॉम आवेश के किसी चालक से 1 सेकंड में प्रवाहित होती है।
1 ऐम्पियर =1 कूलॉम/1सेकंड
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 3:
Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
एक कूलॉम आवेश की रचना करने वाले इलेक्ट्रॉनों की संख्या का परिकलन कीजिए।
Answer
Charge on one electron, e = 1.6 x 10-19 C
Total charge, Q = 1 C
Number of electrons, n = \(\frac{Q}{e} = \frac{1C}{1.6 \times 10^{-19}} = 6.25 \times 10^8\)
ज्ञात है, 1.6×10-19 कूलॉम आवेश = 1 इलेक्ट्रॉन
अतः , 1 कूलॉम आवेश = \(\frac{1C}{1.6 \times 10^{-19}} = 6.25 \times 10^8\) इलेक्ट्रॉन
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Page No. 174
Question 1:
Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
उस युक्ति का नाम लिखिए, जो किसी चालक के सिरों पर विभवांतर बनाए रखने में सहायता करती है।
Answer
A battery.
सेल अथवा बैटरी।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 2:
What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is 1 V?
यह कहने का क्या तात्पर्य है कि दो बिंदुओं के बीच विभवांतर 1 वोल्ट है?
Answer
It means that 1 J of work is done in moving 1 C charge from one point to the other.
1 वोल्ट विभावांतर का अर्थ है कि एक बिंदु से दूसरे बिंदु तक 1 कूलॉम आवेश को ले जाने में 1 जूल कार्य किया जाता है।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 3:
How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery?
6 वोल्ट बैटरी से गुजरने वाले हर एक कूलॉम आवेश को कितनी ऊर्जा दी जाती है?
Answer
Energy given by battery = charge x potential difference
or W = QV = 1C X 6V = 6J.
विभवांतर, V= 6 वोल्ट; आवेश Q = 1 कूलॉम ऊर्जा
अथवा, कार्य W = VQ= 6×1 = 6 जूल;
अतः V= 6 वोल्ट बैटरी से गुजरने वाले हर एक कूलॉम आवेश को 6 जूल ऊर्जा दी जाती है।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Page No. 181
Question 1:
On what factors does the resistance of a conductor depend?
किसी चालक का प्रतिरोध किन कारकों पर निर्भर करता है?
Answer
The resistance of a conductor depends
(i) on its length (ii) on its area of cross-section and (iii) on the nature of its material.
किसी चालक का प्रतिरोध (R) निम्न कारकों पर निर्भर करता है।
(i) चालक की लम्बाई (l)
(ii) अनुप्रस्थ-काट का क्षेत्रफल (A)
(iii) चालक के पदार्थ की प्रकृति
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 2:
Will current flow more easily through a thick wire or a thin wire of the same material, when connected to the same source? Why?
समान पदार्थ के दो तारों में यदि एक पतला तथा दूसरा मोटा हो, तो इनमें से किसमें विद्युत धारा आसानी से प्रवाहित होगी, जबकि उन्हें समान विद्युत स्रोत से संयोजित किया जाता है, क्यों?
Answer
The relation between resistance and the area of cross section can be given as:
R \(\propto \frac{1}{A}\).
Resistance is inversely proportional to the area of cross-section of the wire.
As the resistance decreases, the current increases.
Thicker the wire, less current will pass through it whereas thinner the wire, more current will pass.
किसी तार का प्रतिरोध (R) उसके अनुप्रस्थ-काट के क्षेत्रफल (A) के व्युत्क्रमानुपाती होता है। जो तार मोटा है, उसका अनुप्रस्थ-काट का क्षेत्रफल A अधिक है, अतः प्रतिरोध कम है। यही कारण है कि मोटे तार में से विद्युत धारा अधिक सरलता से प्रवाहित होगी।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 3:
Let the resistance of an electrical component remains constant while the potential difference across the two ends of the component decreases to half of its former value. What change will occur in the current through it?
मान लीजिए किसी वैद्युत अवयव के दो सिरों के बीच विभवांतर को उसके पूर्व के विभवांतर की तुलना में घटा कर आधा कर देने पर भी उसका प्रतिरोध नियत रहता है। तब उस अवयव से प्रवाहित होने वाली विद्युत धारा में क्या परिवर्तन होगा?
Answer
According to Ohm’s law
V = IR
⇒ I = \(\frac{V}{R}\) … (1)
Now Potential difference is decreased to half
∴ New potential difference Vʹ=\(\frac{V}{2}\)
Resistance remains constant
So the new current Iʹ = \(\frac{V’}{R}\)
= \(\frac{\frac{V}{2}}{R}\) (V/2)/R
= \(\frac{1}{2} \frac{V}{R}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) I = \(\frac{l}{2}\)
Therefore, the amount of current flowing through the electrical component is reduced by half.
प्रथम दशा में, यदि दिए गए विद्युत अवयव का प्रतिरोध = R ओम तथा उसके दो सिरों के बीच विभवांतर = V वोल्ट है।
तब विद्युत धारा = ऐम्पियर होगी।
दूसरी दशा में,
प्रतिरोध = R ओम; V’ = \(\frac{V}{2}\) वोल्ट
विद्युत धारा , I‘ = \(\frac{V}{2} \times \frac{1}{2} = \frac{V}{2R}\)
= \(\frac{\frac{V}{2}}{R}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2} \frac{V}{R}\)
= \(\frac{1}{2}\) I = \(\frac{l}{2}\)
र्थात् विभवांतर आधा करने पर विद्युत धारा भी पहले की अपेक्षा आधी हो जाएगी।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 4:
Why are coils of electric toasters and electric irons made of an alloy rather than a pure metal?
विद्युत टोस्टरों तथा विद्युत इस्तरियों के तापन अवयव शुद्ध धातु के न बना कर किसी मिश्रधातु के क्यों बनाए जाते हैं?
Answer
The coils of electric toasters, electric irons and other heating devices are made of an alloy rather than a pure metal because the resistivity of an alloy is much higher than that of a pure metal.
मिश्रधातुओं की प्रतिरोधकता अपनी अवयवी धातुओं की अपेक्षा अधिक होती है। | इसीलिए मिश्रधातुओं का उच्च ताप पर उपचयन (दहन) नहीं होता। अतः इनका उपयोग विद्युत टोस्टरों, इस्तरियों आदि के तापन अवयव के अवयव बनाने हेतु किया जाता है।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 5:
Use the data in Table 11.2 to answer the following –
(a) Which among iron and mercury is a better conductor?
(b) Which material is the best conductor?
निम्न प्रश्नों के हल सारणी में दिए हुए आँकड़ों के आधार पर कीजिए।
(a) आयरन (Fe) तथा मरकरी (Hg) में कौन अच्छा विद्युत चालक है?
(b) कौन-सा पदार्थ सर्वश्रेष्ठ चालक है?
Answer
(i) Resistivity of iron = 10.0 x 10-8 Ω m
Resistivity of mercury = 94.0 x 10-8 Ω m.
Thus iron is a better conductor because it has lower resistivity than mercury.
(ii) Because silver has the lowest resistivity (= 1.60 x 10-8 Ω m), therefore, silver is the best conductor.
(a) आयरन (Fe) की विद्युत प्रतिरोधकता = 10.0×10-18 ओम-मी
मर्करी (Hg) की विद्युत प्रतिरोधकता = 94.0×10-8 ओम-मी
आयरन मर्करी की अपेक्षा अच्छा विद्युत चालक है क्योंकि इसकी प्रतिरोधकता अपेक्षाकृत कम है।
(b) सिल्वर (प्रतिरोधकता = 1.60×10-8ओम-मी) सर्वश्रेष्ठ चालक है, क्योंकि इसकी प्रतिरोधकता सबसे कम है।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Page No. 185
Question 1:
Draw a schematic diagram of a circuit consisting of a battery of three cells of 2 V each, a 5 W resistor, an 8 W resistor, and a 12 W resistor, and a plug key, all connected in series.
किसी विद्युत परिपथ का व्यवस्था आरेख खींचिए, जिसमें 2 वोल्ट के तीन सेलों की बैटरी, जो 52 प्रतिरोध, 8 ओम प्रतिरोध व ओम 12 ओम प्रतिरोध तथा एक प्लग कुँजी सभी श्रेणीक्रम में संयोजित हों।
Answer
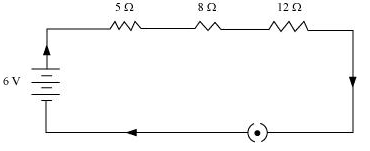
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 2:
Redraw the circuit of Question 1, putting in an ammeter to measure the current through the resistors and a voltmeter to measure the potential difference across the 12 W resistor. What would be the readings in the ammeter and the voltmeter?
प्रश्न 1 का परिपथ आरेख दोबारा खींचिए तथा इसमें प्रतिरोधकों से प्रवाहित विद्युत धारा को मापने के लिए अमीटर तथा 12 ओम के प्रतिरोधक के सिरों के बीच विभवांतर मापने के लिए वोल्टमीटर लगाइए। अमीटर तथा वोल्टमीटर के क्या पाठ्यांक होंगे?
Answer
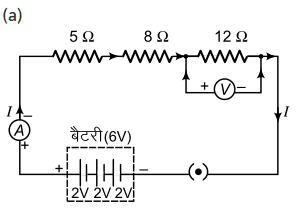
Potential difference, V = 6 V
Current flowing through the circuit/resistors = I
Resistance of the circuit, R = 5 + 8 + 12 = 25Ω
I = \(\frac{V}{R}\) = \(\frac{6}{25}\) = 0.24 A
Potential difference across 12 Ω resistor = V1
Current flowing through the 12 Ω resistor, I = 0.24 A
Therefore, using Ohm’s law, we obtain
V1 = IR = 0.24 x 12 = 2.88 V
Therefore, the reading of the ammeter will be 0.24 A.
The reading of the voltmeter will be 2.88 V.
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Page No. 188
Question 1:
Judge the equivalent resistance when the following are connected in parallel –
(a) 1 W and 106 W, (b) 1 W and 103 W, and 106 W.
जब (a) 1 ओम तथा 106 ओम (b) 1 ओम, 103 ओम तथा 106 ओम के प्रतिरोध समांतर क्रम में संयोजित किए जाते हैं, तो इनके तुल्य प्रतिरोध के संबंध में आप क्या निर्णय करेंगे?
Answer
जब विभिन्न प्रतिरोधों को समांतर क्रम में संयोजित किया जाता है, तब तुल्य प्रतिरोध सबसे कम प्रतिरोध से भी कम होता है, अतः
(a) तुल्य प्रतिरोध <1 ओम
(b) तुल्य प्रतिरोध >1 ओम
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 2:
An electric lamp of 100 W, a toaster of resistance 50 W, and a water filter of resistance 500 W are connected in parallel to a 220 V source. What is the resistance of an electric iron connected to the same source that takes as much current as all three appliances, and what is the current through it?
100 ओम का एक विद्युत लैम्प, 50 ओम का एक विद्युत टोस्टर तथा 500 ओम का एक जल फिल्टर 220 वोल्ट के विद्युत स्रोत से समांतर क्रम में संयोजित है। उस विद्युत इस्तरी का प्रतिरोध क्या हैं जिसे यदि समान स्रोत के साथ संयोजित कर दें, तो वह भी उतनी ही विद्युत धारा लेती हैं जितनी तीनों युक्तियाँ लेती हैं। यह भी ज्ञात कीजिए कि इस विद्युत इस्तरी से कितनी विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है?
Answer
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 3:
What are the advantages of connecting electrical devices in parallel with the battery instead of connecting them in series?
श्रेणीक्रम में संयोजित करने के स्थान पर वैद्युत युक्तियों को समांतर क्रम में संयोजित करने के क्या लाभ हैं?
Answer
वैद्युत युक्तियों को समांतर क्रम में संयोजित करने के निम्न लाभ हैं।
(i) समांतर क्रम में प्रत्येक युक्ति में पूर्ण विद्युत विभव प्राप्त होता है, जबकि धारा विभक्त हो जाती है। प्रत्येक युक्ति में धारा उसके प्रतिरोध के अनुसार जाती है।
(ii) यदि एक युक्ति को ऑन/ऑफ करते हैं, तो अन्य युक्तियाँ अपना कार्य सुचारू रूप से करती रहती हैं।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 4:
How can three resistors of resistances 2 Ω, 3 Ω, and Ω W be connected to give a total resistance of (a) 4 Ω, (b) 1 Ω?
2 ओम, 3 ओम तथा 6 ओम के तीन प्रतिरोधों को किस प्रकार संयोजित करेंगे कि संयोजन का कुल प्रतिरोध (a) 4 ओम (b) 1 ओम हो?
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 5:
What is (a) the highest, (b) the lowest total resistance that can be secured by combinations of four coils of resistance 4 Ω, 8 Ω, 12 Ω, 24 Ω?
4 ओम, 8 ओम, 12 ओम तथा 24 ओम प्रतिरोध की चार कुंडलियों को किस प्रकार संयोजित करें कि संयोजन से (a) अधिकतम (b) निम्नतम प्रतिरोध प्राप्त हो सके?
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Page No. 190
Question 1:
Why does the cord of an electric heater not glow while the heating element does?
किसी विद्युत हीटर की डोरी क्यों उत्तप्त नहीं होती, जबकि उसका तापन अवयव उत्तप्त हो जाता है?
Answer
तापन अवयव तथा डोरी दोनों में ही समान विद्युत धारा प्रवाहित होती है, मगर डोरी का बाह्य भाग एक कुचालक पदार्थ से बना होता है, जिसकी प्रतिरोधकता बहुत अधिक होती है तथा इसी कारण प्रतिरोध भी। हीटर का तापन अवयव सुचालक धातु (मिश्रधातु) से निर्मित अर्थात् कम प्रतिरोधकता (तथा प्रतिरोध) वाला होता है। इसलिए यह उत्तप्त हो जाता है मगर डोरी उत्तप्त नहीं होती।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 2:
Compute the heat generated while transferring 96000 coulomb of charge in one hour through a potential difference of 50 V.
एक घंटे में 50 वोल्ट विभवांतर से 96000 कूलॉम आवेश को स्थानान्तरित करने में उत्पन्न ऊष्मा परिकलित कीजिए।
Answer
V = 50 वोल्ट, t = 1 घंटा, Q = 96000 कूलॉम
H = VIt (परन्तु I =Q/t)
अतः
H = V×Q = 50×96000 = 4800000 जूल = 4800 किलोजूल
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 3:
An electric iron of resistance 20 Ω takes a current of 5 A. Calculate the heat developed in 30 s.
20 ओम प्रतिरोध की कोई विद्युत इस्तरी 5 ऐम्पियर विद्युत धारा लेती है। 30 सेकंड में उत्पन्न ऊष्मा को परिकलित कीजिए।
Answer
R = 20 ओम, I = 5 ऐम्पियर; t = 30 सेकंड
उत्पन्न ऊष्मा (H) = I2Rt = 5×5×20×30 = 15000 जूल = 15 किलोजूल
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Page No. 192
Question 1:
What determines the rate at which energy is delivered by a current?
विद्युत धारा द्वारा प्रदत्त ऊर्जा की दर का निर्धारण कैसे किया जाता है?
Answer
विद्युत धारा द्वारा प्रदत्त ऊर्जा की दर को विद्युत शक्ति (P) भी कहते हैं।
विद्युत शक्ति, P = I2R = VI = V2/R = H/t
जहाँ I विद्युत धारा, R प्रतिरोध, V विभवांतर, H ऊष्मा तथा t समय है।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 2:
An electric motor takes 5 A from a 220 V line. Determine the power of the motor and the energy consumed in 2 h.
कोई विद्युत मोटर 220 वोल्ट के विद्युत स्रोत से 5.0 ऐम्पियर विद्युत धारा लेता है। मोटर की शक्ति निर्धारित कीजिए तथा 2 घंटे में मोटर द्वारा उपमुक्त ऊर्जा परिकलित कीजिए।
Answer
V = 220 वोल्ट, I = 5.0 ऐम्पियर
t = 2 घंटे = 2×60×60 = 7200 सेकंड
(i) मोटर की शक्ति P = V×I = 220×5.0 = 1100 वाट = 1.1 किलोवाट
(ii) मोटर द्वारा उपमुक्त ऊर्जा, H = P×t
= 1100×7200 = 7920000 जूल
= 7.92×106 जूल = 7.9×103 किलोजूल
अथवा
उपमुक्त ऊर्जा, H = P×t
= 1.1 किलोवाट × 2 घंटा
= 22 किलोवाट-घंटा
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Page No. 193
Exercise
Question 1:
A piece of wire of resistance R is cut into five equal parts. These parts are then connected in parallel. If the equivalent resistance of this combination is R¢, then the ratio R/R’ is –
प्रतिरोध R के किसी तार के टुकड़े को पाँच बराबर भागों में काटा जाता है। इन टुकड़ों को फिर समांतरक्रम में संयोजित कर देते हैं। यदि संयोजन का तुल्य प्रतिरोध R’ है, तो R/R’ अनुपात का मान क्या है?
(a) 1/25 (b) 1/5 (c) 5 (d) 25
Answer
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 2:
Which of the following terms does not represent electrical power in a circuit?
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा पद विद्युत परिपथ में विद्युत शक्ति को निरूपित नहीं। करता?
(a) I2R (b) IR2 (c) VI (d) V2/R
Answer
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 3:
An electric bulb is rated 220 V and 100 W. When it is operated on 110 V, the power consumed will be –
किसी विद्युत बल्ब का अनुमतांक 220 वोल्ट 100 वाट है। जब इसे 110 वोल्ट पर प्रचालित करते हैं, तब इसके द्वारा उपमुक्त शक्ति कितनी होती है?
(a) 100 W (b) 75 W (c) 50 W (d) 25 W
Answer
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 4:
Two conducting wires of the same material and of equal lengths and equal diameters are first connected in series and then parallel in a circuit across the same potential difference. The ratio of heat produced in series and parallel combinations would be –
दो चालक तार जिनके पदार्थ, लंबाई तथा व्यास समान हैं, किसी विद्युत परिपथ में पहले श्रेणीक्रम में और फिर समांतर क्रम में संयोजित किए जाते हैं। श्रेणीक्रम तथा समांतर क्रम संयोजन में उत्पन्न ऊष्माओं का अनुपात क्या होगा?
(a) 1:2 (b) 2:1 (c) 1:4 (d) 4:1
Answer
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 5:
How is a voltmeter connected in the circuit to measure the potential difference between two points?
Answer
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 6:
A copper wire has diameter 0.5 mm and resistivity of 1.6 × 10–8 W m. What will be the length of this wire to make its resistance 10 W? How much does the resistance change if the diameter is doubled?
Question 7:
The values of current I flowing in a given resistor for the corresponding values of potential difference V across the resistor are given below –
I (amperes) 0.5 1.0 2.0 3.0 4.0
V (volts) 1.6 3.4 6.7 10.2 13.2
Plot a graph between V and I and calculate the resistance of that resistor.
Question 8:
When a 12 V battery is connected across an unknown resistor, there is a current of 2.5 mA in the circuit. Find the value of the resistance of the resistor.
Question 9:
A battery of 9 V is connected in series with resistors of 0.2 W, 0.3 W, 0.4 W , 0.5 W and 12 W, respectively. How much current would flow through the 12 W resistor?
Question 10:
How many 176 W resistors (in parallel) are required to carry 5 A on a 220 V line?
Question 11:
Show how you would connect three resistors, each of resistance 6 W, so that the combination has a resistance of (i) 9 W, (ii) 4 W.
Question 12:
Several electric bulbs designed to be used on a 220 V electric supply line, are rated 10 W. How many lamps can be connected in parallel with each other across the two wires of 220 V line if the maximum allowable current is 5 A?
Question 13:
A hot plate of an electric oven connected to a 220 V line has two resistance coils A and B, each of 24 W resistance, which may be used separately, in series, or in parallel. What are the currents in the three cases?
Question 14:
Compare the power used in the 2 W resistor in each of the following circuits:
(i) a 6 V battery in series with 1 W and 2 W resistors, and (ii) a 4 V battery in parallel with 12 W and 2 W resistors.
Answer
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-11 Electricity विद्युत

