NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-6 Tissues
Page No. 61
Question 1:
What is a tissue?
ऊतक क्या है?
Answer
A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue.
वे कोशिकाएँ जो आकृत्ति में एक सामान होती है तथा किसी कार्य को एक साथ संपन्न करती हैं, समूह में एक ऊतक का निर्माण करती हैं ।
Question 2:
What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
बहुकोशिक जीवों में ऊतकों का क्या उपयोग है?
Answer
In multicellular organisms there are millions of cells. Most of these cells are specialised to carry out specific functions. Each specialised function is taken up by a different group of cells. Since these cells carry out only a particular function, they do it very efficiently.
बहुकोशिक जीवों में लाखो कोशिकाएँ होती है। इनमें से अधिकतर कोशिकाएँ कुछ विशिष्ट कार्यों को ही संपन्न करने में सक्षम होती है। प्रत्येक विशेष कार्य कोशिकाओं विभिन्न समूहों द्वारा किया जाता है। कोशिकाओं के ये समूह एक विशिष्ट कार्य को ही अति दक्षता पूर्वक संपन्न करने के लिए सक्षम होते हैं।
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-6 Tissues
Page No. 65
Question 1:
Name types of simple tissues.
सरल ऊतकों के कितने प्रकार हैं?
Answer
The types of simple tissues are as follows:
(1) Parenchyma
(2) Collenchyma
(3) Sclerenchyma
सरल ऊतकों के प्रकार इस प्रकार हैं:
(1) पैरेन्काइमा
(2) कॉलेन्काइमा
(3) स्क्लेरेन्काइमा
Question 2:
Where is apical meristem found? [Imp.]
प्ररोह का शीर्षस्थ विभज्योतक कहाँ पाया जाता है?
Answer
Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots and increases the length of the stem and the root.
प्ररोह के शीर्षस्थ विभज्योतक जड़ों एवं तनों की वृद्धि वाले भाग में विद्यमान रहता है तथा वह इनकी लम्बाई में वृद्धि करता है।
Question 3:
Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
नारियल का रेशा किस ऊतक का बना होता है?
Answer
The husk of a coconut is made of sclerenchymatous tissue.
नारियल का रेशा स्क्लेरेन्काइमा ऊतक का बना होता है।
Question 4:
What are the constituents of phloem?
फ़्लोएम के संघटक कौन-कौन से हैं?
Answer
Phloem is made up of five types of cells:
(1) sieve cells,
(2) sieve tubes,
(3) companion cells,
(4) phloem fibres and
(5) phloem parenchyma.
फ्लोएम पांच प्रकार के अवयवों: चालनी कोशिकाएं, चालनी नलिका , साथी कोशिकाएं , फ्लोएम पैरेन्काइमा तथा फ्लोएम रेशों से मिलकर बना होता है।
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-6 Tissues
Page No. 69
Question 1:
Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
उस ऊतक का नाम बताएँ जो हमारे शरीर में गति के लिए उत्तरदायी है|
Answer
Muscular tissue
पेशीय ऊतक|
Question 2:
What does a neuron look like?
न्यूरॉन देखने में कैसा लगता है?
Answer
A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hair-like parts arise.
न्यूरॉन देखने में पूँछ सहित तारे के आकार का ऊतक लगता है|
Question 3:
Give three features of cardiac muscles. [Imp.]
हृदय पेशी के तीन लक्षणों को बताएँ|
Answer
Three features of cardiac muscles (heart muscles) are:
(1) The muscles of the heart show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life.
(2) These involuntary muscles are called cardiac muscles.
(3) Heart muscle cells are cylindrical, branched and uninucleate.
हृदय पेशी के तीन लक्षण निम्नलिखित हैं :
(1) हृदय पेशियाँ अनैच्छिक पेशियाँ हैं जो जीवन भर लयबद्ध होकर प्रसार एवं संकुचन करती रहती हैं|
(2) हृदय की पेशी कोशिकाएँ बेलनाकार, शाखाओं वाली होती हैं |
(3) हृदय पेशी कोशिकाएँ एक-केंद्रकीय होती हैं|
Question 4:
What are the functions of areolar tissue? [Imp.]
एरिओलर ऊतक के क्या कार्य हैं?
Answer
The functions of areolar tissue are:
(1) Areolar connective tissue is found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow.
(2) It fills the space inside the organs, supports internal organs and helps in repair of tissues.
एरिओलर ऊतक के कार्य :
(1) यह आंतरिक अंगों को सहारा प्रदान करता है|
(2) यह अंगों के भीतर खाली जगह को भरता है और ऊतकों की मरम्मत में सहायता करता है|
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-6 Tissues
Page No. 70
Exercise
Question 1:
Define the term “tissue”.
ऊतक को परिभाषित करें|
Answer
A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue.
ऊतक कोशिकाओं का वह समूह है, जिनकी संरचना एक समान होती है तथा जो विशिष्ट कार्य को अतिदक्षता पूर्वक संपन्न करने के लिए एक साथ संगठित होते हैं|
Question 2:
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
कितने प्रकार के तत्व मिलकर ज़ाइलम ऊतक का निर्माण करते हैं? उनके नाम बताएँ|
Answer
Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres.
ज़ाइलम ऊतक का निर्माण चार प्रकार के तत्वों से होता है :
(1) ट्रैकीड् (वाहिनिका)
(2) वाहिका
(3) ज़ाइलम पैरेन्काइमा
(4) ज़ाइलम फाइबर
Question 3:
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
पौधों में सरल ऊतक जटिल ऊतक से किस प्रकार भिन्न होते हैं?
Answer
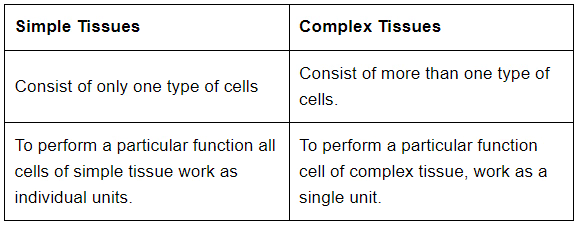

Question 4:
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall. [Imp.]
कोशिका भित्ति के आधार पर पैरेन्काइमा, कॉलेन्काइमा, स्क्लेरेन्काइमा के बीच भेद स्पष्ट करें|
Answer
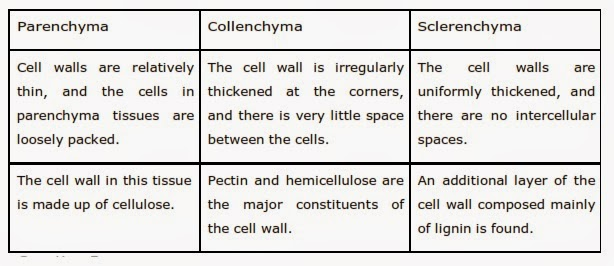

Question 5:
What are the functions of the stomata?
रंध्र के क्या कार्य हैं?
Answer
The functions of stomata are:
(1) They are necessary for exchanging gases with the atmosphere.
(2) Transpiration (loss of water in the form of water vapour) also takes place through stomata.
रंध्र के कार्य :
(1) ये कोशिकाएँ वायुमंडल से गैसों का आदान-प्रदान करते हैं|
(2) वाष्पोत्सर्जन की क्रिया भी रंध्र के द्वारा होती है|
Question 6:
Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
तीन प्रकार के पेशीय रेशों में चित्र बनाकर अंतर स्पष्ट करें|
Answer
The three types of muscle fibres are: Striated muscles, smooth muscles (unstriated muscle fibre), and cardiac muscles.
तीन प्रकार के पेशीय रेशे हैं: (a) रेखित पेशी; (b) चिकनी पेशी; तथा (c) कार्डिक (हृदयक पेशी)|
Question 7:
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
कार्डिक (हृदयक) पेशी का विशेष कार्य क्या है?
Answer
Function of cardiac muscles are:
(1) The muscles of the heart show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life.
(2) These involuntary muscles are called cardiac muscles.
(3) Heart muscle cells are cylindrical, branched and uninucleate.
हृदय पेशियों के विशिष्ट कार्य जीवन भर लयबद्ध होकर हृदय के प्रसार एवं संकुचन को नियंत्रित करना है|
Question 8:
Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
रेखित, अरेखित तथा कार्डिक (हृदयक) पेशियों में शरीर में स्थित कार्य और स्थान के आधार पर अंतर स्पष्ट करें|
Answer
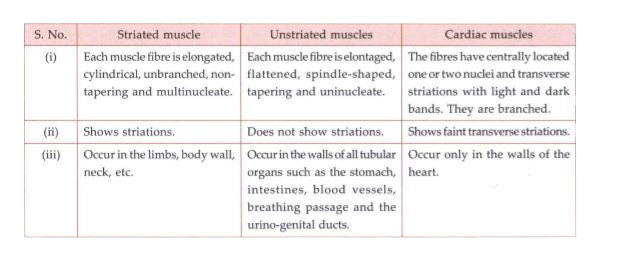

Question 9:
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
न्यूरॉन का एक चिन्हित चित्र बनाएँ|
Answer
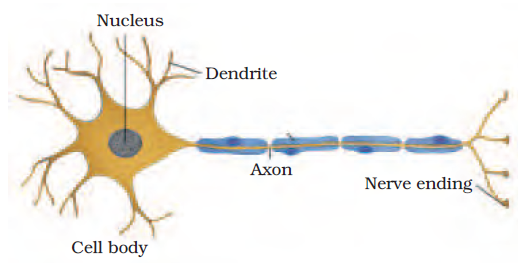
Question 10:
Name the following.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
निम्नलिखित के नाम लिखें :
(a) ऊतक जो मुँह के भीतरी अस्तर का निर्माण करता है |
(b) ऊतक जो मनुष्य में पेशियों को अस्थि से जोड़ता है |
(c) ऊतक जो पौधों में भोजन का संवहन करता है |
(d) ऊतक जो हमारे शरीर में वसा का संचय करता है |
(e) तरल अधात्री सहित संयोजी ऊतक |
(f) मस्तिष्क में स्थित ऊतक |
Answer
(a) Epithelium Tissue एपिथीलियम ऊतक
(b) Tendon कंडरा
(c) Phloem फ़्लोएम
(d) Areolar tissue वसामय ऊतक
(e) Blood रक्त
(f) Nervous tissue तंत्रिका ऊतक
Question 11:
Identify the type of tissue in the following:
skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
निम्नलिखित में ऊतक के प्रकार की पहचान करें :
त्वचा, पौधे का वल्क, अस्थि, वृक्कीय नलिका अस्तर, संवहन बंडल |
Answer
(a) Skin—Striated squamous epithelium
(b) Bark of tree—Cork, protective tissue
(c) Bone—Connective tissue
(d) Lining of kidney tubule—Cuboidal epithelium tisse
(e) Vascular bundle—Conducting tissue
(a) त्वचा- शल्की एपिथीलियम ऊतक
(b) पौधे का वल्क- सरल स्थायी ऊतक
(c) अस्थि- संयोजी ऊतक
(d) वृक्कीय नलिका अस्तर- घनाकार एपिथीलियम ऊतक
(e) संवहन बंडल- जटिल स्थायी ऊतक
Question 12:
पैरेन्काइमा ऊतक किस क्षेत्र में स्थित होते हैं?
Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer
Leaves, fruits, and flowers are the regions where the parenchyma tissue is present.
पत्तियाँ, फल और फूल ऐसे क्षेत्र हैं जहां पैरेन्काइमा ऊतक स्थित होते हैं|
Question 13:
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
पौधों में एपीडर्मिस की क्या भूमिका है?
Answer
Epidermisis present on the outer surface of the entire plant body which perform following role:
(1) It is a protective tissue of the plant body.
(2) It protects the plant against mechanical injury.
(3) It allows exchange of gases through the stomata.
पौधों की बाह्य सतह पर उपस्थित एपीडर्मिस की निम्नलिखित भूमिका है :
(1) यह पौधों की प्रतिरोधी ऊतक है|
(2) यह जल हानि के विरूद्ध यांत्रिक आघात तथा परजीवी कवक के प्रवेश से पौधों की रक्षा करती है|
(3) यह स्टोमेटा के द्वारा गैसों के आदान-प्रदान में सहायता करता है|
Question 14:
How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
छाल (कॉर्क) किस प्रकार सुरक्षा ऊतक के रूप में कार्य करता है?
Answer
The outer protective layer or bark of a tree is known as the cork. It is made up of dead cells. Therefore, it protects the plant against mechanical injury, temperature extremes, etc. It also prevents the loss of water by evaporation.
एक पेड़ की बाह्य सुरक्षात्मक परत को छाल (कॉर्क) कहा जाता है| इन छालों की कोशिकाएँ मृत होती हैं| इस प्रकार यह पौधों की यांत्रिक आघात, अत्यधिक तापमान से सुरक्षा करता है| यह वाष्पीकरण द्वारा होने वाले पानी की हानि को रोकता है|
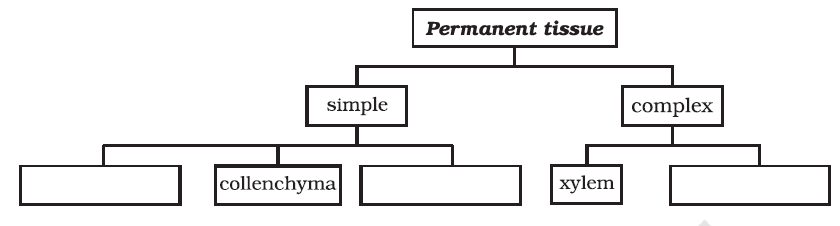
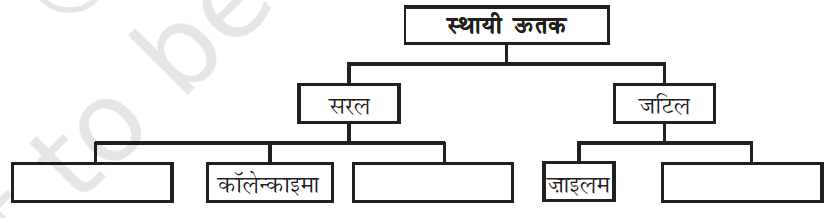
Question 15:
Complete the table:
निम्न दी गई तालिका को पूर्ण करें:
Answer
Simple: Parenchyma, Collenchyma, Sclerenchyma
Complex: Xylem, and Phloem
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-6 Tissues

