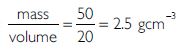NCERT Solution of Class 9 Science Ch-9 Gravitation
Page No. 102
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Question 1:
State the universal law of gravitation.
Answer
The universal law of gravitation states that every object in the universe attracts every other object with a force called the gravitational force. The force acting between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between their centers.
Question 2:
Write the formula to find the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and an object on the surface of the earth.
Answer
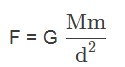
where,
F = force of attraction
G = constant of proportionality
M = mass of earth
m = mass of the object
d = distance between the earth’s centre and object’s centre.
NCERT Solution of Class 9 Science Ch-9 Gravitation
Page No. 104
Question 1:
What do you mean by free fall?
Answer
Whenever objects fall towards the earth under this force alone, we say that the objects are in free fall.
Question 2:
What do you mean by acceleration due to gravity?
Answer
When an object falls towards the ground from a height, then its velocity changes during the fall. This changing velocity produces acceleration in the object. This acceleration is known as acceleration due to gravity (g). Its value is given by 9.8 m/s2.
NCERT Solution of Class 9 Science Ch-9 Gravitation
Page No. 106
Question 1:
What are the differences between the mass of an object and its weight?
Answer
| Mass | Weight |
| Mass is the quantity of matter contained in the body. | Weight is the force of gravity acting on the body. |
| It is the measure of the inertia of the body. | It is the measure of gravity. |
| It only has magnitude. | It has magnitude as well as direction. |
| Mass is a constant quantity. | Weight is not a constant quantity. It is different in different places. |
| Its SI unit is kilogram (kg). | Its SI unit is the same as the SI unit of force, i.e., Newton (N). |
Question 2:
Why is the weight of an object on the moon 1/6th its weight on the earth?
Answer
The mass of moon is 1/100 times and its radius 1/4 times that of earth. As a result, the gravitional attraction on the moon is about one sixth when compared to earth. Hence, the the weight of an object on the moon 1/6th its weight on the earth.
NCERT Solution of Class 9 Science Ch-9 Gravitation
Page No. 109
Question 1:
Why is it difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string?
Answer
It is difficult to hold a school bag having a strap made of a thin and strong string because as the surface area of the string in contact with the shoulders is very less and due to this, its weight applies a large pressure on the shoulders.
Question 2:
What do you mean by buoyancy?
Answer
The upward force possessed by a liquid on an object that’s immersed in it is referred to as buoyancy.
Question 3:
Why does an object float or sink when placed on the surface of water?
OR
Why does iron nail sink while a cork floats on the surface of water? [Imp.]
Answer
An object floats or sinks when placed on the surface of water because of two reasons:
(i) If its density is greater than that of water, an object sinks in water.
(ii) If its density is less than that of water, an object floats in water.
NCERT Solution of Class 9 Science Ch-9 Gravitation
Page No. 110
Question 1:
You find your mass to be 42 kg on a weighing machine. Is your mass more or less than 42 kg?
Answer
When we weigh our body, an upward force acts on it. This upward force is the buoyant force. As a result, the body gets pushed slightly upwards, causing the weighing machine to show a reading less than the actual value.
Question 2:
You have a bag of cotton and an iron bar, each indicating a mass of 100 kg when measured on a weighing machine. In reality, one is heavier than other. Can you say which one is heavier and why?
Answer
The cotton bag is heavier than the iron bar. The cotton bag experiences larger up thrust of air than the iron bar. So, the weighing machine indicates a smaller mass for cotton bag than its actual mass.
NCERT Solution of Class 9 Science Ch-9 Gravitation
Page No. 111
Exercise
Question 1:
How does the force of gravitation between two objects change when the distance between them is reduced to half ?
Answer
According to Universal Law of gravitation, the gravitational force of attraction between any two objects of mass M and m is proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of distance r between them
So, force F is given by

Hence, if the distance is reduced to half, then the gravitational force becomes four times larger than the previous value.
Question 2:
Gravitational force acts on all objects in proportion to their masses. Why then, a heavy object does not fall faster than a light object?
Answer
All objects fall on ground with constant acceleration, called acceleration due to gravity (in the absence of air resistances). It is constant and does not depend upon the mass of an object. Hence, heavy objects do not fall faster than light objects.
Question 3:
What is the magnitude of the gravitational force between the earth and a 1 kg object on its surface? (Mass of the earth is 6 × 1024 kg and radius of the earth is 6.4 × 106 m.)
Answer
Given that,
Mass of the body, m= 1 kg
Mass of the Earth, M= 6×1024 kg
Radius of the earth, R= 6.4×106 m
Now, magnitude of the gravitational force (F) between the earth and the body can be calculated.

Question 4:
The earth and the moon are attracted to each other by gravitational force. Does the earth attract the moon with a force that is greater or smaller or the same as the force with which the moon attracts the earth? Why?
Answer
According to the universal law of gravitation, two objects attract each other with equal force, but in opposite directions. The Earth attracts the moon with an equal force with which the moon attracts the earth.
Question 5:
If the moon attracts the earth, why does the earth not move towards the moon?
Answer
The Earth and the moon experience equal gravitational forces from each other. However, the mass of the Earth is much larger than the mass of the moon. Hence, it accelerates at a rate lesser than the acceleration rate of the moon towards the Earth. For this reason, the Earth does not move towards the moon.
Question 6:
What happens to the force between two objects, if
(i) the mass of one object is doubled?
(ii) the distance between the objects is doubled and tripled?
(iii) the masses of both objects are doubled?
Answer
From Universal law of gravitation, force exerted on an object of mass m by earth is given by

So as the mass of any one of the object is doubled the force is also doubled.
(ii) The force F is inversely proportional to the distance between the objects. So if the distance between two objects is doubled then the gravitational force of attraction between them is reduced to one fourth(1/4) of its original value.
Similarly, if the distance between two objects is tripled, then the gravitational force of attraction becomes one ninth(1/9) of its original value.
(iii) Force F is directly proportional to the product of both the masses. So, if both the masses are doubled then the gravitational force of attraction becomes four times the original value.
Question 7:
What is the importance of universal law of gravitation?
Answer
The importance of universal law of gravitaion?
(i) the force that binds us to the earth;
(ii) the motion of the moon around the earth;
(iii) the motion of planets around the Sun; and
(iv) the tides due to the moon and the Sun.
Question 8:
What is the acceleration of free fall?
Answer
Acceleration of free fall is the acceleration produced when a body falls under the influence of the force of gravitation of the earth alone. It is denoted by g and its value on the surface of the earth is 9.8 ms-2.
Question 9:
What do we call the gravitational force between the earth and an object?
Answer
Gravitational force between the earth and an object is known as the weight of the object.
Question 10:
Amit buys few grams of gold at the poles as per the instruction of one of his friends. He hands over the same when he meets him at the equator. Will the friend agree with the weight of gold bought? If not, why? [Hint: The value of g is greater at the poles than at the equator.]
Answer
Weight of a body on the Earth is given by:
W = mg
Where,
m = Mass of the body
g = Acceleration due to gravity
The value of gis greater at poles than at the equator. Therefore, gold at the equator weighs less than at the poles. Hence, Amit’s friend will not agree with the weight of the gold bought.
Question 11:
Why will a sheet of paper fall slower than one that is crumpled into a ball?
Answer
When a sheet of paper is crumbled into a ball, then its density increases. Hence, resistance to its motion through the air decreases and it falls faster than the sheet of paper.
Question 12:
Gravitational force on the surface of the moon is only 1/6 as strong as gravitational force on the earth. What is the weight in newtons of a 10 kg object on the moon and on the earth?
Answer
Weight of an object on the moon = 1/6 ×Weight of an object on the Earth
Also,
Weight = Mass × Acceleration
Acceleration due to gravity, g = 9.8 m/s2
Therefore, weight of a 10 kg object on the Earth = 10 × 9.8 = 98 N
And, weight of the same object on the moon= 1.6 × 9.8 = 16.3 N.
Question 13: [Important]
A ball is thrown vertically upwards with a velocity of 49 m/s.
Calculate
(i) the maximum height to which it rises,
(ii) the total time it takes to return to the surface of the earth.
Answer
According to the equation of motion under gravity:
v2 – u2 = 2gs
At maximum height, final velocity of the ball is zero, i.e., v= 0
u = 49 m/s
During upward motion, g = -9.8 m s-2
Let h be the maximum height attained by the ball.
Hence,
0 – 492 = 2×9.8×h
⇒ h = 492/(2×9.8)
⇒ h = 2401/19.6 = 122.5
Let t be the time taken by the ball to reach the height 122.5 m, then according to the equation of motion:
v = u + gt
We get,
0 = 49 + t x (- 9.8)
9.8t = 49
t = 49 / 9.8 = 5s
Also,
Time of ascent = Time of descent
Therefore, total time taken by the ball to return = 5 + 5 = 10 s
Question 14:
A stone is released from the top of a tower of height 19.6 m. Calculate its final velocity just before touching the ground.
Answer
According to the equation of motion under gravity:
v2 − u2 = 2 gs
Where,
u = Initial velocity of the stone = 0
v = Final velocity of the stone
s = Height of the stone = 19.6 m
g = Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m s-2
∴ v2 − 02 = 2 × 9.8 × 19.6
v2 = 2 × 9.8 × 19.6 = (19.6)2
v = 19.6 m s-1
Hence, the velocity of the stone just before touching the ground is 19.6 m s-1.
Question 15:
A stone is thrown vertically upward with an initial velocity of 40 m/s. Taking g = 10 m/s2, find the maximum height
reached by the stone. What is the net displacement and the total distance covered by the stone?
Answer
Given data:
Initial velocity u = 40m/s g = 10 m/s 2
Max height final velocity = 0
Consider the third equation of motion v 2 = u 2 – 2gs [negative as the object goes up]
0 = (40) 2 – 2 x 10 x s s = (40 x 40) / 20
Maximum height s = 80m
Total Distance = s + s = 80 + 80
Total Distance = 160m
Total displacement = 0 (The first point is the same as the last point)
Question 16:
Calculate the force of gravitation between the earth and the Sun, given that the mass of the earth = 6 × 1024 kg and of the Sun = 2 × 1030 kg. The average distance between the two is 1.5 × 1011 m.
Answer
Given data:
Mass of the sun m s = 2 × 10 30 kg
Mass of the earth m e = 6 × 10 24 kg
Gravitation constant G = 6.67 x 10 -11 N m 2 / kg 2
Average distance r = 1.5 × 10 11 m
Consider the Universal law of Gravitation
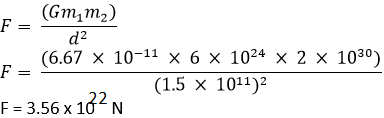
Question 17:
A stone is allowed to fall from the top of a tower 100 m high and at the same time another stone is projected vertically upwards from the ground with a velocity of 25 m/s. Calculate when and where the two stones will meet.
Answer
(i) When the stone from the top of the tower is thrown,
Initial velocity u’ = 0
Distance traveled = x
Time taken = t
Therefore,

(ii) When the stone is thrown upwards, Initial velocity u = 25 m/s Distance travelled = (100 – x) Time taken = t

From equations (a) and (b)
5t 2 = 100 -25t + 5t 2 t = (100/25) = 4sec.
After 4sec, two stones will meet From (a) x = 5t 2 = 5 x 4 x 4 = 80m.
Putting the value of x in (100-x) = (100-80) = 20m.
This means that after 4sec, 2 stones meet a distance of 20 m from the ground.
Question 18:
A ball thrown up vertically returns to the thrower after 6 s.
Find
(a) the velocity with which it was thrown up,
(b) the maximum height it reaches, and
(c) its position after 4 s.
Answer
(a) The velocity with which ball was thrown up :
Acceleration due to gravity, g = – 9.8 ms–2
As the total time taken in upward and return journey by the ball is 6 s.
Therefore, The upward journey, t = 6/2 s = 3 s
Final velocity, v = 0 ms–1
Initial velocity, u = ?
Using equation of motion, v = u + at,
we have
0 = u + (−9.8 × 3)
⇒ u = 9.8 × 3
⇒ u = 29.4 m/s
Hence, the ball was thrown upwards with a velocity of 29.4 m/s.
(b) Let the maximum height attained by the ball be s.
Initial velocity during the upward journey, u = 29.4 m/s
Final velocity, v = 0 m/s
Acceleration due to gravity, g = −9.8 ms−2
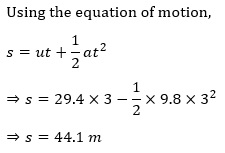
Hence, the maximum height is 44.1 m.
(c) Ball attains the maximum height after 3s. After attaining this height, it will start falling downwards.
In this case,
Initial velocity, u = 0 m/s
Position of the ball after 4 s of the throw is given by the distance travelled by it during its downward journey in 4 s − 3 s = 1 s.

Now, total height = 44.1 m
This means, the ball is 39.2 m (44.1 m − 4.9 m) above the ground after 4 seconds.
NCERT Solution of Class 9 Science Ch-9 Gravitation
Question 19:
In what direction does the buoyant force on an object immersed in a liquid act?
Answer
The buoyant force on an object that is immersed in a liquid will be in a vertically upward direction.
Question 20:
Why does a block of plastic released under water come up to the surface of water?
Answer
Water has a higher density than plastic does. Consequently, the buoyancy force exerted on the plastic block will surpass its weight. Therefore, the plastic block will accelerate in an upward direction. The plastic block therefore reaches the water’s surface.
Question 21:
The volume of 50 g of a substance is 20 cm³. If the density of water is 1 g cm–3, will the substance float or sink?
Answer
Density of substance =
The density of substance (2.5 gcm-3) is more than that of water (1 gcm-3). Therefore, the substance will sink to the bottom.
Question 22:
The volume of a 500 g sealed packet is 350 cm³. Will the packet float or sink in water if the density of water is 1 g
cm–3? What will be the mass of the water displaced by this packet?
Answer
Density of packet =
Since the density of packet is more than that of water, therefore, the packet will sink to the bottom.
Mass of water displaced = Volume of water displaced × density of water
i.e.,
or m = 350 g
NCERT Solution of Class 9 Science Ch-9 Gravitation