NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Page No. 105
Question 1:
What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया तथा टहलने के बीच क्या अंतर है?
Answer
| Reflex Action | Walking |
| 1. It is an involuntary action. | 1. It is a voluntary action. |
| 2. It occurs automatically and instantly in response to a stimulus. | 2. It is performed under conscious control. |
| 3. It is controlled by the spinal cord. | 3. It is controlled by the brain. |
| प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया | टहलने |
| 1. यह अनैच्छिक क्रिया होती है। | 1. यह स्वैच्छिक क्रिया होती है। |
| 2. यह अचानक किसी उत्तेजना के प्रति होती है। | 2. यह सोच-समझ कर की जाती है। |
| 3. यह मेरुरज्जु द्वारा नियंत्रित होती है। | 3. यह मस्तिष्क द्वारा नियंत्रित होती है। |
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination
Question 2:
What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
दो तंत्रिका कोशिकाओं (न्यूरॉन) के मध्य अन्तर्ग्रथन (सिनेप्स) में क्या होता है?
Answer
The synapse is the tiny gap (not seen by naked eyes) between two adjacent neurons. This information, acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body, and then along the axon to its end.
दो तंत्रिका कोशिकाओं (न्यूरॉन) के मध्य एक रिक्त स्थान होता है, जिसे सिनेप्स (सिनेप्टिक दरार) कहते हैं| एक्सॉन के अंत में विद्युत् आवेग कुछ रसायनों का विमोचन कराता है| ये रसायन रिक्त स्थान या सिनेप्स (सिनेप्टिक दरार) को पार करते हैं और अगली तंत्रिका कोशिका की द्रुमिका में इसी तरह का विद्युत् आवेग प्रारंभ करते हैं|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination
Question 3:
Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
मस्तिष्क का कौन सा भाग शरीर की स्थिति तथा संतुलन का अनुरक्षण करता है?
Answer
Cerebellum
अनुमस्तिष्क
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination
Question 4:
How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
हम एक अगरबत्ती की गंध का पता कैसे लगाते हैं?
Answer
When agarbatti burns, it produces pleasant smell, which is detected by the olfactory receptor present inside the nose. The action of smell generates the electrical impulse. These impulses are carried to the sensory area of brain(forebrain-cerebrum). Thus we detect the smell of agarbatti.
जब अगरबत्ती की गंध हमारी नाक तक पहुँचती है तो हमारे नाक में मौजूद घ्राणग्राही इसका पता लगाकर विद्युत् आवेग के द्वारा अग्रमस्तिष्क को इसकी जानकारी भेजता है| अग्रमस्तिष्क मस्तिष्क का सोचने वाला भाग होता है और इसकी सहायता से हम अगरबत्ती की गंध का पता लगा सकते हैं|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination
Question 5:
What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया में मस्तिष्क की क्या भूमिका है?
Answer
Reflex action occurs in spinal cord. The brain and spinal cord constitute the central nervous system. They receive information from all parts of the body and integrate it.
पर्यावरण में किसी घटना की अनुक्रिया के फलस्वरूप अचानक हुई अनैच्छिक क्रिया को प्रतिवर्ती क्रिया कहते हैं| इस क्रिया में कोई ग्राही सूचना ग्रहण कर इसे अभिवाही तंत्रिका तंतु से होते हुए मेरुरज्जु में संयोजी तंत्रिका तंतु के माध्यम से प्रवाही अंग तक पहुँचाता है|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination
Page No. 108
Question 1:
What are plant hormones?
पादप हॉर्मोन क्या है?
Answer
The chemical substances produced in plants which control growth, development and responses in plants, are called plants plant hormones.
For example: Auxins, Gibberellins, Cytokinins and Abscisic acid.
पादप हॉर्मोन पौधों में वृद्धि, विकास तथा पर्यावरण के प्रति अनुक्रिया के समन्वय में सहायता करते हैं| जब वृद्धि करता पादप प्रकाश को संसूचित करता है, एक हॉर्मोन जिसे ऑक्सिन कहते हैं, यह प्ररोह के अग्रभाग में संश्लेषित होता है तथा कोशिकाओं की लंबाई में वृद्धि में सहायक होता है|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination
Question 2:
How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
छुई-मुई पादप की पत्तियों की गति, प्रकाश की ओर प्ररोह की गति से किस प्रकार भिन्न है?
Answer
| Movements of leaves of sensitive plants | Movement of a shoot towards light |
| 1. It is not a growth movement. | 1. It is a growth movement. |
| 2. It is a nastic movement which does not depend on the direction of stimulus. | 2. It is a tropic movement which depends on the direction of stimulus. |
छुई-मुई पादप की पत्तियों की गति, प्रकाश की ओर प्ररोह की गति से भिन्न है क्योंकि प्रकाश व प्ररोह गति अनुवर्तन गति होती है जो ऑक्सिन्न हॉर्मोन द्वारा नियंत्रित होती है। परंतु छुई-मुई पादप की पत्तियों छूने के फैलती व सिकुड़ती है जो प्रकाश से नियंत्रित नहीं होती है।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination
Question 3:
Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
एक पादप हॉर्मोन का उदाहरण दीजिए जो वृद्धि को बढ़ाता है|
Answer
Auxin
ऑक्सिन
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Question 4:
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
किसी सहारे के चारों ओर एक प्रतान की वृद्धि में ऑक्सिन किस प्रकार सहायक है?
Answer
Auxin is a plant growth hormone. When the tip of the tendril touches a support, then the auxins present on its tip moves to the side of tip which is away from the support, so, due to more auxins in its tendrils away from the support grows faster.
जब वृद्धि करता पादप प्रकाश को संसूचित करता है, एक हॉर्मोन जिसे ऑक्सिन कहते हैं, प्ररोह के अग्रभाग में संश्लेषित होता है तथा कोशिकाओं की लंबाई में वृद्धि में सहायक होता है| प्ररोह की प्रकाश से दूर वाली दिशा में ऑक्सिन का सांद्रण कोशिकाओं की लंबाई में वृद्धि के लिए उद्दीप्त करता है|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Question 5:
Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
जलानुवर्तन दर्शाने के लिए एक प्रयोग की अभिकल्पना कीजिए|
Answer
Experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism:
(1) Take a porous pot filled with water and bury it in a tray filled with dry soil.
(2) Place a germinating seedling nearby in the soil.
(3) After a few days, observe the direction of root growth.
The roots will grow toward the water source, showing positive hydrotropism.
जलानुवर्तन दर्शाने के लिए प्रयोग – एक पौधा ले उस गमले में उगाए उस की मिट्टी एक ओर से गीली तथा दूसरी ओर से सुखी होनी चाहिए। कुछ दिनों बाद उसका परिक्षण करने पर हम पाएगे की पौध की जड़े जलीय मिट्टी की ओर गतिशील होती है की इस अभिकल्पना से हम पाते है की जड़ों में घनात्मक जलानुवर्तन होता है।
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Page No. 111
Question 1
How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
जंतुओं में रासायनिक समन्वय कैसे होता है?
Answer
Chemical coordination is brought about by chemical messengers called hormones. They are secreted by endocrine glands (ductless glands). The hormones are carried by the blood to the site of action (target organs). The hormones are consumed during their action and provide wide ranging changes.
जंतुओं में रासायनिक समन्वय हॉर्मोन की सहायता से होता है| हार्मोन रासायनिक तरल पदार्थ होते हैं जो अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियों द्वारा स्रावित होते हैं। हार्मोन जानवरों के समग्र विकास और विकास को विनियमित करते हैं|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Question 2:
Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
आयोडीन युक्त नमक के उपयोग की सलाह क्यों दी जाती है?
Answer
Iodine is necessary for the thyroid gland to make thyroxin hormone. Thyroxin regulates carbohydrate, protein and fat, metabolism in the body so as to provide the best balance for growth. Iodine is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin. In case iodine is deficient in our diet, there is a possibility that we might suffer from goitre. One of the symptoms in this disease is a swollen neck.
अवटुग्रन्थि को थायरॉक्सिन हॉर्मोन बनाने के लिए आयोडीन आवश्यक है| थायरॉक्सिन कार्बोहाइड्रेट, प्रोटीन तथा वसा के उपापचय का, हमारे शरीर में नियंत्रण करता है ताकि वृद्धि के लिए उत्कृष्ट अन्तुलन उपलब्ध कराया जा सके| थायरॉक्सिन के संश्लेषण के लिए आयोडीन अनिवार्य है| यदि हमारे आहार में आयोडीन की कमी है तो संभावना है कि हम गायटर से ग्रसित हो सकते हैं| इसलिए आयोडीन युक्त नमक के उपयोग की सलाह दी जाती है|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Question 3:
How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
जब एड्रीनलीन रुधिर में स्रावित होती है तो हमारे शरीर में क्या अनुक्रिया होती है|
Answer
Adrenaline is secreted directly into the blood and carried to different parts of the body. The target organs or the specific tissues on which it acts include the heart. As a result, the heart beats faster, resulting in supply of more oxygen to our muscles.
एड्रीनलीन सीधा रुधिर में स्रावित हो जाता है और शरीर के विभिन्न भागों तक पहुँचा दिया जाता है| हृदय सहित यह लक्ष्य अंगों या विशिष्ट उत्तकों पर कार्य करता है| परिणामस्वरूप हृदय की धड़कन बढ़ जाती है ताकि हमारी पेशियों को अधिक ऑक्सीजन की आपूर्ति हो सके|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Question 4:
Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
मधुमेह के कुछ रोगियों की चिकित्सा इंसुलिन का इंजेक्शन देकर क्यों की जाती है?
Answer
Diabetes patients as a treatment, they might be taking injections of insulin. This is a hormone which is produced by the pancreas and helps in regulating blood sugar levels. If it is not secreted in proper amounts, the sugar level in the blood rises causing many harmful effects.
अग्न्याशय से इंसुलिन हॉर्मोन के उचित मात्रा में स्रावित न होने के कारण मधुमेह नामक बीमारी होती है| ऐसे व्यक्ति के रुधिर में शर्करा स्तर बढ़ जाता है| इंसुलिन रुधिर में मौजूद अतिरिक्त शर्करा को ग्लाइकोजन में परिवर्तित कर देता है| इसलिए मधुमेह के कुछ रोगियों की चिकित्सा इंसुलिन का इंजेक्शन देकर की जाती है|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Page No. 112
Question 1:
Which of the following is a plant hormone?
(a) Insulin
(b) Thyroxin
(c) Oestrogen
(d) Cytokinin.
निम्नलिखित में से कौन-सा पादप हॉर्मोन है?
(a) इंसुलिन
(b) थायरॉक्सिन
(c) एस्ट्रोजन
(d) साइटोकाइनिन
Answer
(d) Cytokinin
(d) साइटोकाइनिन
Question 2:
The gap between two neurons is called a
(a) dendrite.
(b) synapse.
(c) axon.
(d) impulse.
दो तंत्रिका कोशिका के मध्य खाली स्थान को कहते हैं-
(a) द्रुमिका
(b) सिनेप्स
(c) एक्सॉन
(d) आवेग
Answer
(b) synapse
(b) सिनेप्स
Question 3:
The brain is responsible for
(a) thinking.
(b) regulating the heart beat.
(c) balancing the body.
(d) all of the above
मस्तिष्क उत्तरदायी है
(a) सोचने के लिए
(b) हृदय स्पंदन के लिए
(c) शरीर का संतुलन बनाने के लिए
(d) उपरोक्त सभी
Answer
(d) All of the above
(d) उपरोक्त सभी
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Question 4:
What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
हमारे शरीर में ग्राही का क्या कार्य है? ऐसी स्थिति पर विचार कीजिए जहाँ ग्राही उचित प्रकार कार्य नहीं कर रहे हों| क्या समस्याएँ उत्पन्न हो सकती हैं?
Answer
All information from our environment is detected by the specialised tips of some nerve cells. These receptors are usually located in our sense organs, such as the inner ear, the nose, the tongue, and so on. So gustatory receptors will detect taste while olfactory receptors will detect smell.
If olfactory receptor not works properly then we are not able to smell things like aggarbatti, perfumes, flavour of food.
पर्यावरण से सभी सूचनाओं का पता कुछ तंत्रिका कोशिकाओं के विशिष्टीकृत सिरों द्वारा लगाया जाता है| ये ग्राही प्रायः हमारी ज्ञानेन्द्रियों में स्थित होते हैं; जैसे- आन्तरिक कर्ण, नाक जिह्वा आदि| रस संवेदी ग्राही स्वाद का पता लगाते हैं जबकि घ्राणग्राही गंध का पता लगाते हैं|
जहाँ ग्राही उचित प्रकार कार्य नहीं करते हैं वहाँ सुनने, सूँघने तथा स्वाद संबंधी रस का पता नही चलता है|
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Question 5:
Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
एक तंत्रिका कोशिका (न्यूरॉन) की संरचना बनाइए तथा इसके कार्यों का वर्णन कीजिए|
Answer
Structure of a neuron
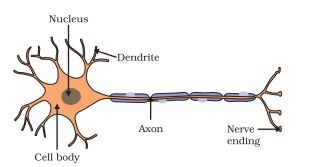
A neurons consists of three parts:
(i) Cell body: It is a typical animal cell which contains cytoplasm and a nucleus.
(ii) Dendrites: A number of long and thin fibres comes out from the cell body of the neurons, they are nerve fibre. The shorter fibres on the cell body of neurons are called dendrites.
(iii) Axon: The longest fibre on the cell body of neurons is called axon. It has an insulating and protective sheath (or cover)of myelin around it.
एक तंत्रिका कोशिका (न्यूरॉन) की संरचना
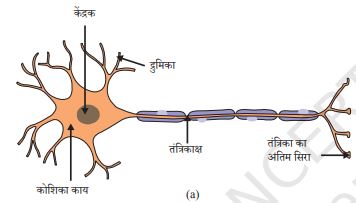
तंत्रिका कोशिका (न्यूरॉन) के कार्य :
सभी सूचनाओं को एक तंत्रिका कोशिका के द्रुमाकृतिक सिरे द्वारा उपार्जित की जाती है और एक रासायनिक क्रिया द्वारा यह एक विद्युत् आवेग पैदा करती है| यह आवेग द्रुमिका से कोशिकाकाय तक जाता है और तब तंत्रिकाक्ष (एक्सॉन) में होता हुआ इसके अंतिम सिरे तक पहुँच जाता है| एक्सॉन के अंत में विद्युत् आवेग कुछ रसायनों का विमोचन कराता है| ये रसायन रिक्त स्थान या सिनेप्स को पार करते हैं और अगली तंत्रिका कोशिका की द्रुमिका में इसी तरह का विद्युत् आवेग प्रारंभ करते हैं| यह शरीर में तंत्रिका आवेग की मात्रा की की सामान्य योजना है| इसी तरह का अंतर्ग्रथन (सिनेप्स) अंततः ऐसे आवेगों को तंत्रिका कोशिका से अन्य कोशिकाओं, जैसे कि पेशी कोशिकाओं या ग्रन्थि तक ले जाता है|
Question 6:
How does phototropism occur in plants?
पादप में प्रकाशानुवर्तन किस प्रकार होता है?
Answer
It is an established fact that plants bend towards light when they are exposed to it from one side of long axis. The aerial parts are positively phototropic and the roots and other underground parts bend away from light. These movements are due to interaction of light and auxins. The unilateral growth causes bending of stem as tip grows more rapidly.
जब किसी तने को प्रकाश की दिशा का पता चलता है, तो ऑक्जिन उस भाग में चला जाता है जो लाइट से दूर हो। इससे छाया में रहने वाले भाग में तेजी से सेल डिविजन होता है। इसका नतीजा यह होता है कि तना प्रकाश की ओर झुक जाता है और प्रकाश की दिशा में बढ़ने लगता है।
Question 7:
Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
मेरुरज्जु आघात में किन संकेतों के आने में व्यवधान होगा?
Answer
Reflex actions are involuntary actions and controlled by the spinal cord thus, gets disrupted in case of spinal cord injury.
मेरुरज्जु आघात में तंत्रिकाओं तथा विभिन्न ग्राही से आने वाले संकेतों में व्यवधान उत्पन्न होगी| चूँकि ये दोनों संकेत मेरुरज्जु में मस्तिष्क को जाने वाले रास्ते में एक बंडल में मिलती है| इसलिए किसी भी मेरुरज्जु के आघात में दोनों संकेतों में बाधा पहुँचती है|
Question 8:
How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
पादप में रासायनिक समन्वय किस प्रकार होता है?
Answer
lants do not have nervous system but still sense the things because of stimulus such as gravity, light, chemicals(hormones), water, touch (touch -me -not plant).Hormones are responsible for the chemical coordination of plants by integrating their behaviour by affecting growth of a plant resulting in movement of that plant part in response to a stimulus.
पादपों में न तो तंत्रिका तंत्र होता है और न ही अन्तःस्रावी तंत्र| लेकिन विभिन्न रासायनिक पदार्थ एक कोशिका से दूसरी कोशिका तक विसरित होते रहते हैं| पादप हॉर्मोन पौधों में वृद्धि, विकास तथा पर्यावरण के प्रति अनुक्रिया के समन्वय में सहायता करते हैं|
Question 9:
What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
एक जीव में नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय के तंत्र की क्या आवश्यकता है?
Answer
Control and Coordination in the body is of two types i.e. nervous control and hormonal control. Nervous control is rapid. It takes place through electrical signals called nerve impulses. The hormonal control is through chemical messengers called hormones secreted by endocrine (ductless) glands and carried by blood to the target organs.
जीवों में विभिन्न अंग होते हैं| जीवों के अस्तित्व के लिए इन अंगों को सावधानीपूर्वक नियंत्रित और समन्वित किया जाना आवश्यक है| जीवों के अंगों में विभिन्न अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियों द्वारा स्रावित हॉर्मोन के द्वारा सूचनाओं के संचरण के साधन की तरह प्रयुक्त होते हैं| ये हॉर्मोन एक जीव के समग्र वृद्धि और विकास के लिए जिम्मेदार होते हैं| इसके अतिरिक्त जीवों में नियंत्रण तथा समन्वय तंत्रिका तथा पेशी उत्तकों द्वारा किया जाता है| आकस्मिक परिस्थिति में गर्म पदार्थ को छूना तथा सभी सूचनाओं को मस्तिष्क तक पहुँचाना जीवों में नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय द्वारा ही संभव है|
Question 10:
How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
अनैच्छिक क्रियाएँ तथा प्रतिवर्ती क्रियाएँ एक-दूसरे से किस प्रकार भिन्न हैं?
Answer
Involuntary actions are not controlled by us they are independent process means there is no stimulus involved in these actions. For example: heart beat, breathing process; etc.
Reflex action is also involuntary in nature but they involves stimulus means functions or respond according to it. For example: stepping out in bright light, changes in size of pupil of eyes.
अनैच्छिक क्रियाएँ वे हैं जिस पर हमारे सोचने का कोई नियंत्रण नहीं है तथा ये अग्र तथा पश्चमस्तिष्क से नियंत्रित होती हैं| जबकि प्रतिवर्ती क्रियाएँ किसी घटना की अनुक्रिया के फलस्वरूप अचानक हुई क्रिया को कहते हैं| ये क्रियाएँ मुख्यतः मेरुरज्जु द्वारा नियंत्रित होते हैं|
Question 11:
Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
जन्तुओं में नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय के लिए तंत्रिका तथा हॉर्मोन क्रियाविधि की तुलना तथा व्यतिरेक कीजिए|
Answer
| Nervous system | Hormonal system |
| 1. Made up of neurons (nerve cell). | 1. Made of secretory cells (glands). |
| 2. Messages transmitted in the form of electrical impulses. | 2. Messages transmitted in the form of chemicals called hormones. |
| 3. Messages transmitted along nerve fibre. | 3. Messages transmitted along blood stream. |
| 4. Effect of message usually lasts for a very short while. | 4. Effect of message usually lasts longer. |
| 5. Messages travel very quickly. | 5. Messages travel more slowly. |
| तंत्रिका तंत्र क्रियाविधि | हॉर्मोन क्रियाविधि |
| यह मस्तिष्क से संवेदी सूचनाओं को प्राप्त कर अपना संदेश भेजता है तथा नियंत्रण करता है| | जंतु हॉर्मोन अंतःस्रावी ग्रंथियों का भाग हैं जो हमारे शरीर में नियन्त्रण एवं समन्वय का दूसरा मार्ग है| |
| यह एक्सॉन के अंत में विद्युत् आवेग का परिणाम है, जो रसायनों का विमोचन कराता है| | इसमें सूचनाओं का संचारण रुधिर के माध्यम से किया जाता है| |
| सूचनाओं का तेजी से प्रवाह होता है तथा प्रतिक्रिया तुरंत होता है| | सूचनाओं का संचारण धीमी गति से होता है तथा प्रतिक्रिया भी धीरे-धीरे होता है| |
| तंत्रिका तंत्र में सूचनाओं को विद्युत् आवेग के द्वारा शरीर के एक भाग से दूसरे भाग तक संवहन में विशिष्टीकृत है| | प्रत्येक हार्मोन की विशिष्ट क्रियाएँ होती हैं| |
| इसका प्रभाव कम समय तक बना रहता है| | इसका लंबे समय तक प्रभाव बना रहता है| |
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय
Question 12:
What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
छुई-मुई पादप में गति तथा हमारी टाँग में होने वाली गति के तरीके में क्या अंतर है?
Answer
The movement of sensitive plants leaves takes place due to the sudden loss of water in the pad-like swelling (called pulvini) at the base of all the leaves. Pulvini limp gets drooped and folded due to the loss of water. On the other hand, the movement of our legs take place due to pull in the muscles of legs on the leg bones.
| छुई-मुई पादप में गति | हमारी टाँग में होने वाली गति |
| एक छुई-मुई पादप में गति उद्दीपन (स्पर्श) की प्रतिक्रिया है, जो एक अनैच्छिक क्रिया है| | हमारी टाँग में होने वाली गति एक स्वैच्छिक क्रिया है| |
| पत्तियों के आकार में भी परिवर्तन होता है| | हमारी टाँगों के आकार में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता| |
| पादप की कोशिकाओं में गति के लिए कोई विशेष प्रोटीन नहीं होता| | जन्तु कोशिकाओं में गति के लिए विशेष प्रोटीन होता है जो कि मांसपेशियों के सिकुड़ने में सहायता करते हैं| |
NCERT Solution of Class 10 Science Ch-6 Control and Coordination नियंत्रण एवं समन्वय

