NCERT Solutions of Class 11 Maths Ch-14 Probability
Exercise 14.1
Question 1:
A die is rolled. Let E be the event “die shows 4” and F be the event “die shows even number”. Are E and F mutually exclusive?
Question 2:
A die is thrown. Describe the following events:
(i) A: a number less than 7 (ii) B: a number greater than 7
(iii) C: a multiple of 3 (iv) D: a number less than 4
(v) E: an even number greater than 4 (vi) F: a number not less than 3
Also find A ∪ B, A ∩ B, B ∪ C, E ∩ F, D ∩ E, A – C, D – E, E ∩ F′, F′
Question 3:
An experiment involves rolling a pair of dice and recording the numbers that come up. Describe the following events:
A: the sum is greater than 8; B: 2 occurs on either die; C: the sum is at least 7 and a multiple of 3.
Which pairs of these events are mutually exclusive?
Question 4:
Three coins are tossed once. Let A denote the event ‘three heads show”, B denote the event “two heads and one tail show”, C denote the event” three tails show and D denote the event ‘a head shows on the first coin”. Which events are
(i) mutually exclusive? (ii) simple? (iii) Compound?
Question 5:
Three coins are tossed. Describe
(i) Two events which are mutually exclusive.
(ii) Three events which are mutually exclusive and exhaustive.
(iii) Two events, which are not mutually exclusive.
(iv) Two events which are mutually exclusive but not exhaustive.
(v) Three events which are mutually exclusive but not exhaustive.
NCERT Solutions of Class 11 Maths Ch-14 Probability
Question 6:
Two dice are thrown. The events A, B and C are as follows:
A: getting an even number on the first die.
B: getting an odd number on the first die.
C: getting the sum of the numbers on the dice ≤ 5.
Describe the events
(i) A′ (ii) not B (iii) A or B
(iv) A and B (v) A but not C (vi) B or C
(vii) B and C (viii) A ∩ B′ ∩ C′
Question 7:
Refer to question 6 above, state true or false: (give reason for your answer)
(i) A and B are mutually exclusive
(ii) A and B are mutually exclusive and exhaustive
(iii) A = B′
(iv) A and C are mutually exclusive
(v) A and B′ are mutually exclusive.
(vi) A′, B′, C are mutually exclusive and exhaustive.
NCERT Solutions of Class 11 Maths Ch-14 Probability
Exercise 14.2
Question 1:
Which of the following can not be valid assignment of probabilities for outcomes of sample Space S = {ω1, ω2, ω3, ω4, ω5, ω6, ω7}
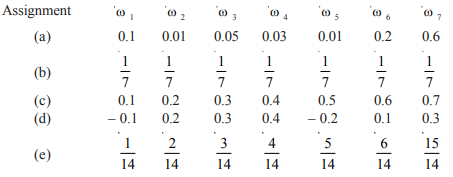
Question 2:
A coin is tossed twice, what is the probability that atleast one tail occurs?
Question 3:
A die is thrown, find the probability of following events:
(i) A prime number will appear,
(ii) A number greater than or equal to 3 will appear,
(iii) A number less than or equal to one will appear,
(iv) A number more than 6 will appear,
(v) A number less than 6 will appear
Question 4:
A card is selected from a pack of 52 cards.
(a) How many points are there in the sample space?
(b) Calculate the probability that the card is an ace of spades.
(c) Calculate the probability that the card is (i) an ace (ii) black card.
NCERT Solutions of Class 11 Maths Ch-14 Probability
Question 5:
A fair coin with 1 marked on one face and 6 on the other and a fair die are both tossed. find the probability that the sum of numbers that turn up is (i) 3 (ii) 12
Question 6:
There are four men and six women on the city council. If one council member is selected for a committee at random, how likely is it that it is a woman?
Question 7:
A fair coin is tossed four times, and a person win Re 1 for each head and lose Rs 1.50 for each tail that turns up.
From the sample space calculate how many different amounts of money you can have after four tosses and the probability of having each of these amounts.
Question 8:
Three coins are tossed once. Find the probability of getting
(i) 3 heads (ii) 2 heads (iii) atleast 2 heads
(iv) atmost 2 heads (v) no head (vi) 3 tails
(vii) exactly two tails (viii) no tail (ix) atmost two tails
Question 9:
If 2/11 is the probability of an event, what is the probability of the event ‘not A’
Question 10:
A letter is chosen at random from the word ‘ASSASSINATION’. Find the probability that letter is (i) a vowel (ii) a consonant
Question 11:
In a lottery, a person choses six different natural numbers at random from 1 to 20, and if these six numbers match with the six numbers already fixed by the lottery committee, he wins the prize. What is the probability of winning the prize in the game? [Hint order of the numbers is not important.]
Question 12:
Check whether the following probabilities P(A) and P(B) are consistently defined
(i) P(A) = 0.5, P(B) = 0.7, P(A ∩ B) = 0.6
(ii) P(A) = 0.5, P(B) = 0.4, P(A ∪ B) = 0.8
Question 13:
Fill in the blanks in following table:
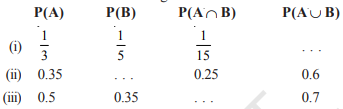
Question 14:
Given P(A) = 3/5 and P(B) = 1/5. Find P(A or B), if A and B are mutually exclusive events.
Question 15:
If E and F are events such that P(E) = 1/4, P(F) = 1/2 and P(E and F) = 1/8, find (i) P(E or F), (ii) P(not E and not F).
Question 16:
Events E and F are such that P(not E or not F) = 0.25, State whether E and F are mutually exclusive.
NCERT Solutions of Class 11 Maths Ch-14 Probability
Question 17:
A and B are events such that P(A) = 0.42, P(B) = 0.48 and P(A and B) = 0.16. Determine (i) P(not A), (ii) P(not B) and (iii) P(A or B)
Question 18:
In Class XI of a school 40% of the students study Mathematics and 30% study Biology. 10% of the class study both Mathematics and Biology. If a student is selected at random from the class, find the probability that he will be studying Mathematics or Biology
Question 19:
In an entrance test that is graded on the basis of two examinations, the probability of a randomly chosen student passing the first examination is 0.8 and the probability of passing the second examination is 0.7. The probability of passing atleast one of them is 0.95. What is the probability of passing both?
Question 20:
The probability that a student will pass the final examination in both English and Hindi is 0.5 and the probability of passing neither is 0.1. If the probability of passing the English examination is 0.75, what is the probability of passing the Hindi examination?
Question 21:
In a class of 60 students, 30 opted for NCC, 32 opted for NSS and 24 opted for both NCC and NSS. If one of these students is selected at random, find the probability that
(i) The student opted for NCC or NSS.
(ii) The student has opted neither NCC nor NSS.
(iii) The student has opted NSS but not NCC.
NCERT Solutions of Class 11 Maths Ch-14 Probability
Miscellaneous Exercise on Chapter 14
Question 1:
A box contains 10 red marbles, 20 blue marbles and 30 green marbles. 5 marbles are drawn from the box, what is the probability that
(i) all will be blue? (ii) atleast one will be green?
Question 2:
4 cards are drawn from a well – shuffled deck of 52 cards. What is the probability of obtaining 3 diamonds and one spade?
Question 3:
A die has two faces each with number ‘1’, three faces each with number ‘2’ and one face with number ‘3’. If die is rolled once, determine
(i) P(2) (ii) P(1 or 3) (iii) P(not 3)
Question 4:
In a certain lottery 10,000 tickets are sold and ten equal prizes are awarded. What is the probability of not getting a prize if you buy (a) one ticket (b) two tickets (c) 10 tickets.
Question 5:
Out of 100 students, two sections of 40 and 60 are formed. If you and your friend are among the 100 students, what is the probability that
(a) you both enter the same section?
(b) you both enter the different sections?
Question 6:
Three letters are dictated to three persons and an envelope is addressed to each of them, the letters are inserted into the envelopes at random so that each envelope contains exactly one letter. Find the probability that at least one letter is in its proper envelope.
Question 7:
A and B are two events such that P(A) = 0.54, P(B) = 0.69 and P(A ∩ B) = 0.35.
Find (i) P(A ∪ B) (ii) P(A´ ∩ B´) (iii) P(A ∩ B´) (iv) P(B ∩ A´)
Question 8:
From the employees of a company, 5 persons are selected to represent them in the managing committee of the company. Particulars of five persons are as follows:
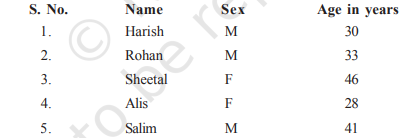
A person is selected at random from this group to act as a spokesperson. What is the probability that the spokesperson will be either male or over 35 years?
Question 9:
If 4-digit numbers greater than 5,000 are randomly formed from the digits 0, 1, 3, 5, and 7, what is the probability of forming a number divisible by 5 when, (i) the digits are repeated? (ii) the repetition of digits is not allowed?
Question 10:
The number lock of a suitcase has 4 wheels, each labelled with ten digits i.e., from 0 to 9. The lock opens with a sequence of four digits with no repeats. What is the probability of a person getting the right sequence to open the suitcase?
NCERT Solutions of Class 11 Maths Ch-14 Probability


Comments are closed.