NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes
Important Questions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Table of Contents
Exercise 12.1
Question 1:
2 cubes each of volume 64 cm3 are joined end to end. Find the surface area of the resulting cuboid.
Solution
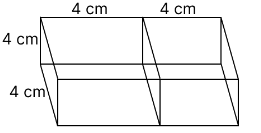
Volume (V) of each cube is = 64 cm3
\(\Rightarrow\) a3 = 64 cm3 = (8)3
∴ a = 4 cm
Now, the side of the cube = a = 4 cm
l = 4 + 4 = 8 cm, b = 4, h = 4 cm
So, the surface area of the cuboid = 2(lb + bh + lh)
\(\quad\quad\) = 2(8 × 4 + 4 × 4 + 4 × 8) cm2
\(\quad\quad\)= 2(32 + 16 + 32) cm2
\(\quad\quad\) = (2 × 80) cm2 = 160 cm2
Question 2:
A vessel is in the form of a hollow hemisphere mounted by a hollow cylinder. The diameter of the hemisphere is 14 cm and the total height of the vessel is 13 cm. Find the inner surface area of the vessel.
Solution
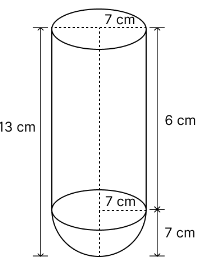
diameter of the hemisphere, d = 14 cm
radius of the hemisphere, r = 7 cm
Also, the height of the cylinder = h = (13-7) = 6 cm
Now, the inner surface area of the vessel
\(\quad\quad\quad\) = CSA of the cylindrical part + CSA of the hemispherical part
\(\quad\quad\quad\)= (2πrh + 2πr2) cm2 = 2πr(h + r) cm2
\(\quad\quad\quad\) = 2×\(\frac{22}{7}\) × 7 (6 + 7) cm2 = 572 cm2
Question 3:
A toy is in the form of a cone of radius 3.5 cm mounted on a hemisphere of same radius. The total height of the toy is 15.5 cm. Find the total surface area of the toy.
Solution
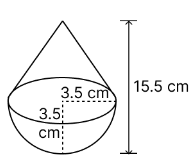
radius of the cone and the hemisphere (r) = 3.5 cm
The total height of the toy = 15.5 cm
So, the height of the cone (h) = 15.5 – 3.5 = 12 cm
slant height of the cone, l = \(\sqrt{h^2 + r^2}\) = \(\sqrt{12^2 + (3.5)^2}\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\)= \(\sqrt{144 + 12.25}\) = \(\sqrt{156.25}\) = 12.5 cm
Now, the Total surface area of the toy = CSA of the cone + CSA of the hemisphere
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = πrl + 2πr2 = πr (l + 2r)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 3.5 (12.5 + 2 × 3.5)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 11 × 19.5 = 214.5 cm2
So, the total surface area (TSA) of the toy is 214.5cm2
Question 4:
A cubical block of side 7 cm is surmounted by a hemisphere. What is the greatest diameter the hemisphere can have? Find the surface area of the solid.
Solution
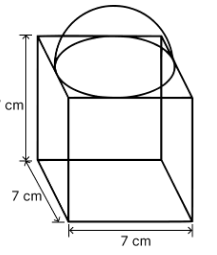
The total surface area of solid (TSA) = surface area of the cubical block + CSA of the hemisphere – Area of the base of the hemisphere
∴ TSA of solid = 6×(side)2+2πr2-πr2
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 6×(side)2+πr2
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 6×(7)2+ \(\frac{22}{7}\) × \(\frac{7}{2}\) × \(\frac{7}{2}\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = (6 × 49) + \(\frac{77}{2}\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 294 + 38.5 = 332.5 cm2
So, the surface area of the solid is 332.5 cm2
Question 5:
A hemispherical depression is cut out from one face of a cubical wooden block such that the diameter l of the hemisphere is equal to the edge of the cube. Determine the surface area of the remaining solid.
Solutiion
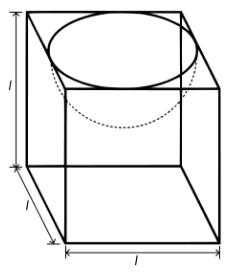
diameter of the hemisphere = Edge of the cube = l
So, the radius of the hemisphere = \(\frac{l}{2}\)
∴ The total surface area of solid = surface area of cube + CSA of the hemisphere – Area of the base of the hemisphere
The surface area of the remaining solid = 6 (edge)2+2πr2-πr2
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 6l2 + πr2
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\)= 6l2+π(\(\frac{l}{2}\))2
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 6l2+π \(\frac{l^2}{4}\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\)= l\(\frac{l^2}{2}\) (24+π) sq. units
Question 6:
A medicine capsule is in the shape of a cylinder with two hemispheres stuck to each of its ends (see Fig. 12.10). The length of the entire capsule is 14 mm and the diameter of the capsule is 5 mm. Find its surface area.
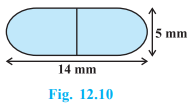
Solution
diameter of the capsule, d = 5 mm
∴ Radius, r = \(\frac{5}{2}\) mm
Now, the length of the capsule = 14 mm
So, the length of the cylinder, h = 14 – (2.5 + 2.5) = 9 mm
Thus, the required surface area of the medicine capsule will be
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = surface area of the cylinder + 2×surface area of hemisphere
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 2πrh + 2 × 2πr2
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 2πr(h + 2r)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 2 × \(\frac{22}{7}\) × \(\frac{5}{2}\) × (9 + 2 × \(\frac{5}{2}\))
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = = 220 mm2.
Hence, surface area of capsule = 220 mm2.
Question 7:
A tent is in the shape of a cylinder surmounted by a conical top. If the height and diameter of the cylindrical part are 2.1 m and 4 m respectively, and the slant height of the top is 2.8 m, find the area of the canvas used for making the tent. Also, find the cost of
the canvas of the tent at the rate of ` 500 per m2 . (Note that the base of the tent will not be covered with canvas.)
Solution
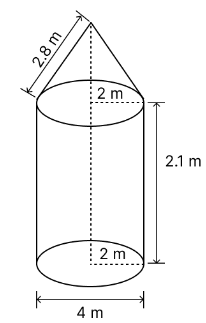
Diameter = 4 m
The slant height of the cone (l) = 2.8 m
Radius of the cone (r) = Radius of cylinder = \(\frac{4}{2}\) = 2 m
Height of the cylinder (h) = 2.1 m
So, the required surface area of the tent = surface area of the cone + surface area of the cylinder
= πrl + 2πrh
= πr (l + 2h)
= \(\frac{22}{7}\) × 2(2.8 + 2 × 2.1)
= \(\frac{44}{7}\) (2.8 + 4.2)
= \(\frac{44}{7}\) × 7 = 44 m2
∴ The cost of the canvas of the tent at the rate of ₹500 per m2 will be
= Surface area × cost per m2
= 44 × 500 = ₹22000
So, ₹ 22000 will be the total cost of the canvas.
Question 8:
From a solid cylinder whose height is 2.4 cm and diameter 1.4 cm, a conical cavity of the same height and same diameter is hollowed out. Find the total surface area of the remaining solid to the nearest cm2.
Solution
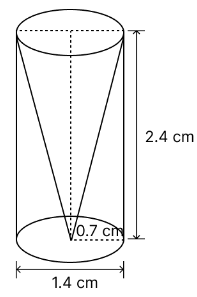
diameter of the cylinder = diameter of conical cavity = 1.4 cm
So, the radius of the cylinder = radius of the conical cavity = 1.4/2 = 0.7
Also, the height of the cylinder = height of the conical cavity = 2.4 cm
slant height of the cone, l = \(\sqrt{h^2 + r^2}\) = \(\sqrt{12^2 + (3.5)^2}\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\)= \(\sqrt{144 + 12.25}\) = \(\sqrt{156.25}\) = 12.5 cm
Now, the TSA of the remaining solid = surface area of conical cavity + TSA of the cylinder
= πrl+(2πrh+πr2) = πr(l+2h+r)
= (22/7)× 0.7(2.5+4.8+0.7) = 2.2×8 = 17.6 cm2
So, the total surface area of the remaining solid is 17.6 cm2
Question 9:
A wooden article was made by scooping out a hemisphere from each end of a solid cylinder, as shown in Fig. 12.11. If the height of the cylinder is 10 cm, and its base is of radius 3.5 cm, find the total surface area of the article.
Solution
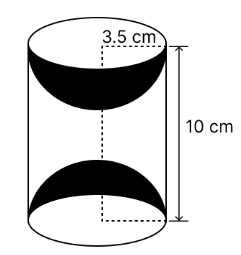
Radius of base of cylinder = Radius of hemisphere = r = 3.5 cm
Total surface area of article = Curved surface area of cylinder + 2 × Curved surface area of each hemisphere
= 2πrh + 2 × 2πr2 = 2πr(h + 2r)
Substituting values we get :
Hence, the total surface area of the article is 374 cm2.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes
Excercise 12.2
Question 1:
A solid is in the shape of a cone standing on a hemisphere with both their radii being equal to 1 cm and the height of the cone is equal to its radius. Find the volume of the solid in terms of \(\pi\).
Solution
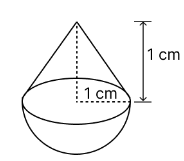
Radius of cone = Radius of hemisphere = r = 1 cm
Height of cone (h) = 1 cm
Volume of solid = Volume of cone + Volume of hemisphere
\(\quad\quad\)
Hence, volume of solid = π cm3.
Question 2:
Rachel, an engineering student, was asked to make a model shaped like a cylinder with two cones attached at its two ends by using a thin aluminium sheet. The diameter of the model is 3 cm and its length is 12 cm. If each cone has a height of 2 cm, find the volume of air contained in the model that Rachel made. (Assume the outer and inner dimensions of the model to be nearly the same.)
Solution
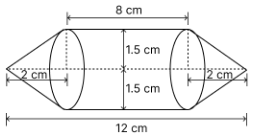
Height of each cone (h) = 2 cm
Diameter of model (d) = 3 cm
Radius of each cone = Radius of cylinder, r = cm
Height of cylinder (H) = 12 – 2 – 2 = 8 cm.
Volume of air inside model = Volume of cylinder + 2 × Volume of each cone
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\)= πr2H +
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = πr2
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = \(\frac{22}{7}\) × \((\frac{3}{2})^2\) × (8 + \(\frac{2}{3} × 2\))
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = \(\frac{22}{7}\) × \(\frac{9}{4}\) × (8 + \(\frac{4}{3}\))
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = \(\frac{22}{7}\) × \(\frac{9}{4}\) × \(\frac{28}{3}\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 66 cm3
Hence volume of air contained in model = 66 cm3.
Question 3:
A gulab jamun, contains sugar syrup up to about 30% of its volume. Find approximately how much syrup would be found in 45 gulab jamuns, each shaped like a cylinder with two hemispherical ends with length 5 cm and diameter 2.8 cm (see Fig. 12.15).
Solution
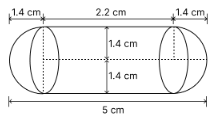
Diameter of gulab jamun (d) = 2.8 cm
Radius of cylindrical portion = Radius of hemispherical portion = r = = 1.4 cm.
Length of cylindrical portion (h) = 5 – 1.4 – 1.4 = 2.2 cm
Volume of each gulab jamun = Volume of cylindrical portion + 2 × Volume of each hemispherical portion
\(\\\)\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = \(\pi r^2 h + 2 \times \frac{2}{3} \pi r^2\)
\(\\\)\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = \(\pi r^2 \left(h + \frac{4}{3} r\right)\)
\(\\\)\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = \(\frac{22}{7} \times (1.4)^2 \times \left(2.2 + \frac{4}{3}\times 1.4\right)\)
\(\\\)\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 6.16\(\times \left(\frac{6.6 + 5.6}{3} \right)\)
\(\\\) \(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 6.16\(\times \left(\frac{12.2}{3} \right)\)
\(\\\) \(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = \(\frac{75.152}{3}\) =25.05 cm3.
Volume of 45 gulab jamuns = 45 × 25.05 = 1127.28 cm3.
Given,
A gulab jamun, contains sugar syrup up to about 30% of its volume.
∴ Sugar syrup in 45 gulab jamuns = 30% of volume of 45 gulab jamuns
= = 338.184 ≈ 338 cm3.
Hence, approximately 338 cm3 of sugar syrup would be found in 45 gulab jamuns.
Question 4:
A pen stand made of wood is in the shape of a cuboid with four conical depressions to hold pens. The dimensions of the cuboid are 15 cm by 10 cm by 3.5 cm. The radius of each of the depressions is 0.5 cm and the depth is 1.4 cm. Find the volume of wood in the entire stand (see Fig. 12.16).
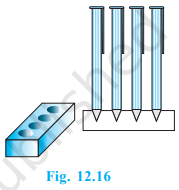
Solution
Length of cuboid (l) = 15 cm
Breadth of cuboid (b) = 10 cm
Height of cuboid (h) = 3.5 cm
Radius of each conical depression (r) = 0.5 cm
Depth of each conical depression (H) = 1.4 cm
From figure,
Volume of wood in stand = Volume of cuboid – 4 × Volume of each conical depression
= lbh – 4 ×
= 15 × 10 × 3.5 –
= 525 –
= 525 –
= 525 – 1.47
= 523.53 cm3.
Hence, volume of wood in entire stand = 523.53 cm3.
Question 5:
A vessel is in the form of an inverted cone. Its height is 8 cm and the radius of its top, which is open, is 5 cm. It is filled with water up to the brim. When lead shots, each of which is a sphere of radius 0.5 cm are dropped into the vessel, one-fourth of the water flows out. Find the number of lead shots dropped in the vessel.
Solution
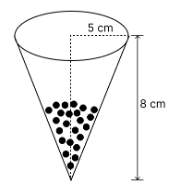
Radius of cone (R) = 5 cm
Height of cone (H) = 8 cm
Volume of cone =
Substituting values we get :
Volume of water in vessel = Volume of cone = cm3.
Let no. of lead shots be n.
Given,
Radius of lead shots (r) = 0.5 cm
Since,
One-fourth of the water flows out after dropping lead shots in vessel.
∴ n × Volume of each lead shot = Volume of water
\(\Rightarrow\) n × \(\frac{4}{3} \pi r^3\) = \(\frac{1}{4} × \frac{200 \pi}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) n × \(\frac{4}{3} \pi (0.5)^3\) = \(\frac{50 \pi}{3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) n = \(\frac{50 \pi × 3}{4\pi × 3 × (0.5)^3}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) n = \(\frac{50}{4 × 0.125}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) n = \(\frac{50}{0.5}\)
\(\Rightarrow\) n = 100
Hence, 100 lead shots were dropped in vessel.
Question 6:
A solid iron pole consists of a cylinder of height 220 cm and base diameter 24 cm, which is surmounted by another cylinder of height 60 cm and radius 8 cm. Find the mass of the pole, given that 1 cm3 of iron has approximately 8g mass. (Use \(\pi\) = 3.14)
Solution
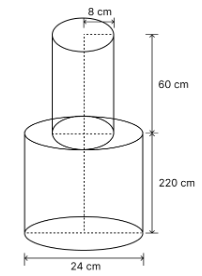
For bigger cylinder :
Diameter (d) = 24 cm
Radius (R) = = 12 cm.
Height (H) = 220 cm
Volume = πR2H
= 3.14 × (12)2 × 220
= 3.14 × 144 × 220
= 99475.20 cm3
For smaller cylinder :
Radius (r) = 8 cm
Height (h) = 60 cm
Volume = πr2h
= 3.14 × 82 × 60
= 3.14 × 64 × 60
= 12057.60 cm3.
Volume of pole = Volume of bigger cylinder + Volume of smaller cylinder
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 99475.20 + 12057.60 = 111532.80 cm3
Given,
1 cm3 of iron weighs 8 g.
∴ Mass of pole = Volume of pole × 8 g
= 111532.80 × 8 = 892262.4 g
=
= 892.26 kg.
Hence, mass of pole = 892.26 kg.
Question 7:
A solid consisting of a right circular cone of height 120 cm and radius 60 cm standing on a hemisphere of radius 60 cm is placed upright in a right circular cylinder full of water such that it touches the bottom. Find the volume of water left in the cylinder, if the radius of the cylinder is 60 cm and its height is 180 cm.
Solution
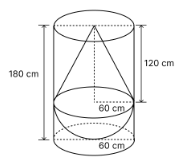
Height of right circular cone (h) = 120 cm
Height of cylinder (H) = 180 cm
Radius of cylinder = Radius of cone = Radius of hemisphere = r = 60 cm.
Volume of water left in cylinder = Volume of cylinder – Volume of solid
= Volume of cylinder – (Volume of cone + Volume of hemisphere)
= \(\pi r^2 H – \left(\frac{1}{3} \pi r^2 h + \frac{2}{3} \pi r^3\right)\)
= \(\pi r^2 \left(H – \frac{h}{3} – \frac{2}{3} r\right)\)
= \(\frac{22}{7} × 60^2 \left(180 – \frac{120}{3} – \frac{2}{3} × 60\right)\)
= \(\frac{22}{7} × 3600 × \left(180 – 40 – 40\right)\)
= \(\frac{22}{7} × 3600 × 100\)
= \(\frac{7920000}{7}\)
= 1131428.57143 cm3
= 1131428.57143 × 10−6 m3
= 1.131 m3.
Hence, volume of water left in cylinder = 1.131 m3.
Question 8:
A spherical glass vessel has a cylindrical neck 8 cm long, 2 cm in diameter; the diameter of the spherical part is 8.5 cm. By measuring the amount of water it holds, a child finds its volume to be 345 cm3 . Check whether she is correct, taking the above as the inside
measurements, and \(\pi\) = 3.14.
Solution
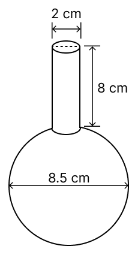
Diameter of sphere (D) = 8.5 cm
Radius of sphere (R) = = 4.25 cm.
Height of cylindrical neck (h) = 8 cm
Diameter of cylindrical neck (d) = 2 cm
Radius of cylindrical neck (r) = = 1 cm.
Volume of glass vessel = Volume of sphere + Volume of cylinder
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\quad\) = \(\frac{4}{3} \pi R^3 + \pi r^2 h\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\quad\) = \(\pi \left(\frac{4}{3} R^3 + r^2 h\right)\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\quad\) = 3.14 × \(\left(\frac{4}{3} (4.25)^3 + 1^2 × 8\right)\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\quad\) = 3.14 × \(\left(\frac{4}{3} × 76.77 + 1 × 8\right)\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\quad\) = 3.14 × \(\left(\frac{307.0625}{3} + 8\right)\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\quad\) = 3.14 × \(\left(102.35 + 8\right)\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\quad\) = 3.14 × \(\left(110.35\right)\)
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\qquad\quad\) =346.51 cm3.
∴ Volume of water in vessel = 346.51 cm3.
Hence, volume of water in vessel is not equal to 345 cm3.
NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 12 Surface Areas and Volumes

