Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds कार्बन एवं उसके यौगिक
Question 1:
What are covalent bonds? Show their formation with the help of electron dot structure of methane. Why are covalent compounds generally poor conductors of electricity?
सहसंयोजक बंध क्या होते हैं? मीथेन के इलेक्ट्रॉन बिंदु संरचना की सहायता से इनके निर्माण को दर्शाइए। सहसंयोजक यौगिक सामान्यतः विद्युत के कुचालक क्यों होते हैं?
Answer
Covalent bonds are those bonds which are formed by sharing of the valence electrons between two atoms. Electron dot structure of methane is shown in the figure.
वे बंध जो दो परमाणुओं के बीच संयोजक इलेक्ट्रॉनों के साझाकरण (sharing) द्वारा बनते हैं, उन्हें सहसंयोजक बंध कहा जाता है।
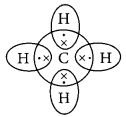
Covalent compounds are generally poor conductors ol electricity because they do not have tree electrons or ions.
सहसंयोजक यौगिक सामान्यतः विद्युत के कमजोर चालक होते हैं, क्योंकि इनमें मुक्त इलेक्ट्रॉन (free electrons) या आयन (ions) नहीं होते हैं जो विद्युत धारा का वहन कर सकें।
Question 2:
Give reasons for the following:
(i) Element carbon forms compounds mainly by covalent bonding.
(ii) Diamond has high melting point.
(iii) Graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
निम्नलिखित के कारण बताइए :
(i) तत्व कार्बन मुख्यतः सहसंयोजक बंध द्वारा यौगिक क्यों बनाता है?
(ii) हीरे का गलनांक बहुत अधिक क्यों होता है?
(iii) ग्रेफाइट विद्युत का अच्छा चालक क्यों है?
Answer
(i) As carbon has four valence electrons and it can neither loose nor gain lour electrons thus, it attains noble gas configuration only by sharing of electrons. I bus, it forms covalent compounds.
(i) कार्बन के पास चार संयोजक इलेक्ट्रॉन होते हैं। यह न तो चार इलेक्ट्रॉन खो सकता है और न ही चार इलेक्ट्रॉन प्राप्त कर सकता है, क्योंकि ऐसा करने से बहुत अधिक ऊर्जा की आवश्यकता होगी। इसलिए यह इलेक्ट्रॉनों के साझाकरण (sharing) द्वारा सहसंयोजक बंध बनाता है और इस प्रकार निष्क्रिय गैस संरचना (noble gas configuration) प्राप्त करता है।
(ii) In diamond, each carbon atom is bonded to four other carbon atoms forming a rigid three-dimensional structure. This makes diamond the hardest known substance. Thus, it has high melting point.
(ii) हीरे (Diamond) में प्रत्येक कार्बन परमाणु चार अन्य कार्बन परमाणुओं से सहसंयोजक बंध द्वारा जुड़ा होता है, जिससे एक कठोर त्रि-आयामी संरचना बनती है। यह संरचना बहुत मजबूत होती है, इसलिए हीरा सबसे कठोर पदार्थ है और उसका गलनांक बहुत अधिक होता है।
(iii) In graphite, each carbon atom is bonded to three other carbon atoms by covalent bonds in the same plane giving a hexagonal array. Thus, only three valence electrons are used for bond formation and hence, the fourth valence electron is free to move. As a result, graphite is a good conductor of electricity.
(iii) ग्रेफाइट (Graphite) में प्रत्येक कार्बन परमाणु तीन अन्य कार्बन परमाणुओं से सहसंयोजक बंध बनाता है और षट्कोणीय परतों का निर्माण करता है। प्रत्येक कार्बन का चौथा संयोजक इलेक्ट्रॉन स्वतंत्र रहता है, जो परतों के बीच स्वतंत्र रूप से गतिशील होता है। इसी कारण ग्रेफाइट विद्युत का अच्छा चालक (good conductor of electricity) होता है।
Question 3:
Write the next homologue of each of the following:
निम्नलिखित के प्रत्येक का अगला समावयवी लिखिए :
(i) C2H4
(ii) C4H6
Answer
(i) C2H4 belongs to alkene series having general formula, CnH2n.
Thus, next homologue will be C3H2×3 = C3H6
C₂H₄ एल्कीन श्रेणी से संबंधित है, जिसका सामान्य सूत्र होता है — CnH2n
अतः, अगला समावयवी होगा — C3H2×3 = C3H6
(ii) C4H6 belongs to alkyne series having general formula, CnH2n-2.
Thus, next homologue will be C5H2×5-2 = C5H8
C₄H₆ एल्काइन श्रेणी से संबंधित है, जिसका सामान्य सूत्र होता है —CnH2n-2.
अतः, अगला समावयवी होगा — C5H2×5-2 = C5H8
Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 4 Carbon and its Compounds कार्बन एवं उसके यौगिक

