Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 11 Electricity विद्युत
Question 1:
How do we express electric current?
हम विद्युत धारा को कैसे व्यक्त करते हैं?
Answer
Electric current is expressed by the amount of charge flowing through a particular area in unit time. In other words, it is the rate of flow of electric charges.
विद्युत धारा को एकांक समय में किसी विशेष क्षेत्र से प्रवाहित आवेश के परिमाण द्वारा व्यक्त किया जाता है। दूसरे शब्दों में, विद्युत आवेशों के प्रवाह की दर को विधीत धार कहते है।
Question 2:
In an electric circuit, state the relationship between the direction of conventional current and the direction of flow of electrons.
एक विद्युत परिपथ में परम्परागत धारा की दिशा तथा इलेक्ट्रॉनों के प्रवाह की दिशा के बीच संबंध बताइए।
Answer
In an electric circuit the direction of flow of electrons is opposite to the direction of flow of current. The direction of flow of current is considered to be the direction of flow of positive charge known as conventional current. The current flows from higher potential to lower potential in an electric circuit.
एक विद्युत परिपथ में इलेक्ट्रॉनों के प्रवाह की दिशा धारा के प्रवाह की दिशा के विपरीत होती है। धारा के प्रवाह की दिशा को परम्परागत धारा के रूप में जाना जाने वाला धनावेशों के प्रवाह की दिशा माना जाता है। विद्युत परिपथ में विद्युत धारा उच्च विभव से निम्न विभव की ओर प्रवाहित होती है।
Question 3:
Distinguish between conductors and insulators.
चालकों एवं विद्युतरोधी में अन्तर स्पष्ट कीजिए।
Answer
Conductors: Conductors are the substances through which electric charges can flow easily.
चालक : चालक वे पदार्थ हैं जिनके माध्यम से विद्युत आवेश आसानी से प्रवाहित हो सकते हैं।
Insulators: Insulators are the substances through which electric charges cannot move freely.
विद्युतरोधी: विद्युतरोधी वे पदार्थ हैं जिनके माध्यम से विद्युत आवेश स्वतंत्र रूप से नहीं चल सकते हैं।
Question 4:
Why are metals good conductors of electricity whereas glass is a bad conductor of electricity? Give reason.
धातु विद्युत की सुचालक क्यों होती है जबकि काँच विद्युत का कुचालक होता है? कारण दीजिए।
Answer
Metals have a large number of free electrons which help in the conduction of electricity.
Glass has very few electrons. So it conducts electricity with difficulty.
धातुओं में बड़ी संख्या में मुक्त इलेक्ट्रॉन होते हैं जो विद्युत चालन में सहायता करते हैं।
काँच में बहुत कम इलेक्ट्रॉन होते हैं। इसलिए यह कठिनाई के साथ बिजली का संचालन करता है।
Question 5:
(a) Name the SI unit of electric charge.
(b) State the relationship between 1 ampere and 1 coulomb.
(a) विद्युत आवेश की SI इकाई का नाम बताइए।
(b) 1 ऐम्पियर तथा 1 कूलॉम के बीच संबंध बताइए।
Answer
The SI unit of electric charge is coulomb (C)
विद्युत आवेश की SI इकाई कूलम्ब (C) है
If one coulomb of charge flows through any section of a conductor in one second, then the current through it is said to be one ampere.
एक एम्पीयर विद्युत धारा की रचना प्रति सेकंड एक कूलॉम आवेश के प्रवाह से होती है।
1 ampere = \(\frac{1 Coulomb}{1 Second}\)
\(\quad\) or, 1A = = 1 C s-1
Question 6:
Calculate the number of electrons constituting one coulomb of charge.
एक कूलॉम आवेश बनाने वाले इलेक्ट्रॉनों की संख्या की गणना कीजिए।
Answer
Charge on an electronic, e = 1.6 10 -19 C
Total Charge, Q = 1 C
Number of electrons, n = = 6.25 10 18
इलेक्ट्रॉन पर आवेश, e = 1.6 10 -19 C
कुल आवेश , Q = 1 C
इलेक्ट्रॉनों की संख्या, n = = 6.25 10 18
Question 7:
Define electric current. What is the SI unit of electric current?
विद्युत धारा को परिभाषित कीजिए। विद्युत धारा की SI इकाई क्या है?
Answer
Electric current is expressed by the amount of charge flowing through a particular area in unit time. In other words, it is the rate of flow of electric charges.
Thus, Electric Current = \(\frac{Charge}{Time}\)
\(\quad\) Or, I = \(\frac{Q}{t}\)
The SI unit of electric current is ampere.
विद्युत धारा को एकांक समय में किसी विशेष क्षेत्र से प्रवाहित आवेश के परिमाण द्वारा व्यक्त किया जाता है। दूसरे शब्दों में, विद्युत आवेश के प्रवाह की दर को विद्युत धार कहते हैं।
अतः, विद्युत धारा = \(\frac{आवेश }{समय}\)
\(\quad\) Or, I = \(\frac{Q}{t}\)
Question 8:
(A) What does an electric circuit mean?
(B) Distinguish between an open and a closed circuit.
(A) विद्युत परिपथ क्या है?
(B) खुला तथा बंद परिपथ में अंतर लिखो।
Answer
A continuous and closed path of an electric current is called an electric circuit.
किसी विद्युत धार के सतत तथा बंद पथ को विद्युत परिपथ कहते है।
An electric circuit through which no current flows is called an open circuit.
An electric circuit through which current flows continuously is called a closed circuit.
वह विद्युत परिपथ जिससे होकर कोई धारा प्रवाहित नहीं होती, खुला परिपथ कहलाता है।
वह विद्युत परिपथ जिससे होकर धारा निरंतर प्रवाहित होती है, बंद परिपथ कहलाता है।
Question 9:
What is an ammeter? How is it connected in a circuit?
ऐमीटर क्या है? इसे परिपथ में कैसे जोड़ा जाता है?
Answer
An ammeter is a device used to measure electric current in a circuit.
An ammeter is always connected in series in a circuit, so that entire current, which we wish to measure, flow through it.
ऐमीटर एक उपकरण है जिसका उपयोग किसी परिपथ में विद्युत धारा मापने के लिए किया जाता है। ऐमीटर हमेशा परिपथ में श्रेणीक्रम में जुड़ा होता है, ताकि जिस धारा को हम मापना चाहते हैं, वह पूरी तरह से उसी से प्रवाहित हो।
Question 10:
A current of 0.5 A is drawn by a filament of an electric bulb for 10 minutes. Find the amount of electric charge that flows through the circuit.
किसी विद्युत बल्ब के तन्तु में से 0.5 A विद्युत धारा 10 मिनट तक प्रवाहित होती है। विद्युत परिपथ से प्रवाहित विद्युत आवेश का परिमाण ज्ञात कीजिए।
Answer
We are given, I = 0.5A; t = 10 min = 600s
\(\quad\) Q = It = 0.5A × 600 s = 300 C
Question 11:
An electric bulb draws a current of 0.2A when the voltage is 220 volts. Calculate the amount of electric charge flowing through it in one hour.
एक विद्युत बल्ब 220 वोल्ट होने पर 0.2A धारा खींचता है। एक घंटे में इससे प्रवाहित होने वाले विद्युत आवेश की मात्रा की गणना कीजिए।
Question 12:
The charge possessed by an electron is 1.6 × 10-19 coulomb. Find the number of electrons that flow per second to constitute a current of 1 ampere.
एक इलेक्ट्रॉन का आवेश 1.6 × 10-19 कूलॉम है। 1 एम्पीयर धारा बनाने के लिए प्रति सेकंड प्रवाहित इलेक्ट्रॉनों की संख्या ज्ञात कीजिए।
Question 13:
A charge of 150 coulomb flows through a wire in one minute. Find the electric current flowing through it.
एक तार से 150 कूलॉम आवेश एक मिनट में प्रवाहित होता है। इसमें प्रवाहित विद्युत धारा ज्ञात कीजिए।
Question 14:
Name a device that helps to maintain a potential difference across a conductor.
उस युक्ति का नाम लिखिए, जो किसी चालक के सिरों पर विभवांतर बनाए रखने में सहायता करती है।
Answer
Battery बैटरी
Question 15:
What is meant by saying that the potential difference between two points is 1 V?
यह कहने का क्या तात्पर्य है कि दो बिंदुओं के बीच विभवांतर 1 V है?
Answer
The potential difference between two points is said to be 1 volt if 1 joule of work is done in moving 1 coulomb of electric charge from one point to the other.
दो बिंदुओं के बीच विभवांतर 1 वोल्ट कहा जाता है, यदि 1 कूलॉम विद्युत आवेश को एक बिंदु से दूसरे बिंदु तक ले जाने में 1 जूल कार्य किया जाता है।
Question 16:
How much work is done in moving a charge of 2 C across two points having a potential difference 12 V?
12 V विभवांतर के दो बिन्दुओ के बीच 2 C आवेश को ले जाने में कितना कार्य किया जाता है?
Answer
We are given that, Potential difference (V) = 12 V and Charge (Q) = 2 C
\(\quad\) W = VQ = 12 V × 2 C = 24 J
Question 17:
How much energy is given to each coulomb of charge passing through a 6 V battery?
6 V बैटरी से गुजरने वाले हर एक कूलॉम आवेश को कितनी ऊर्जा दी जाती है?
Answer
We are given that, Potential difference (V) = 6 V and Charge (Q) = 1 C
\(\quad\) W = VQ = 6 V × 1 C = 6 J
Question 18:
Give conventional symbols used for the various electrical components in the circuit diagrams.
परिपथ आरेख में विभिन्न विद्युत घटकों के लिए प्रयुक्त पारंपरिक प्रतीक दीजिए।
5 Marks
Question 1:
Calculate the total cost of running the following electrical devices in the month of September, if the rate of 1 unit of electricity is ₹ 6.00:
(i) Electric heater of 1000 W for 5 hours daily.
(ii) Electric refrigerator of 400 W for 10 hours daily.
यदि 1 यूनिट बिजली की दर 6.00 है तो सितम्बर माह में निम्नलिखित विद्युत उपकरणों को चलाने की कुल लागत ज्ञात कीजिए –
(i) 1000 W का विद्युत हीटर, 5 घंटे प्रतिदिन उपयोग किया गया।
(ii) 400 W का विद्युत रेफ्रीजरेटर, 10 घंटे प्रतिदिन उपयोग किया गया।
Solution
(i) Power, P1 = 1000 W = \(\frac{1000}{1000}\) = 1 KW
\(\quad\) and time, t1 = 5 hours
\(\quad\) Energy, E1 = P1 \(\times\) t1 \(\times\) Number of days
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 1 KW \(\times\) 5 hours \(\times\) 30 days
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 150 KWh
(i) Power, P1 = 400 W = \(\frac{400}{1000}\) = 0.4 KW
\(\quad\) and time, t1 = 10 hours
\(\quad\) Energy, E1 = P1 \(\times\) t1 \(\times\) Number of days
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 0.4 KW \(\times\) 10 hours \(\times\) 30 days
\(\quad\quad\quad\quad\quad\) = 120 KWh
Total Energy = E1 + E2 = 150 + 120 = 270 KWh
Cost of 1 KWh of Energy = ₹ 6
Total Cost = 270 \(\times\) 6 = ₹ 1620
Practice Questions
Question 1:
Calculate the electricity bill for the month of August if:
(i) A fan of 80 W runs for 12 hours daily.
(ii) A television of 200 W runs for 5 hours daily.
(Rate = ₹5 per unit)
अगस्त माह में बिजली खर्च ज्ञात कीजिए यदि
(i) 80 W का पंखा प्रतिदिन 12 घंटे चलता है।
(ii) 200 W का टीवी प्रतिदिन 5 घंटे चलता है।
(दर = ₹5 प्रति यूनिट)
Question 2:
A household uses:
(i) An LED TV of 150 W for 4 hours daily
(ii) A microwave oven of 1200 W for 30 minutes daily
Calculate the monthly electricity bill for September at ₹6 per unit.
एक घर में
(i) 150 W का LED टीवी 4 घंटे
(ii) 1200 W का माइक्रोवेव ओवन 30 मिनट प्रतिदिन
सितम्बर माह का बिजली बिल ज्ञात कीजिए। (दर = ₹6 प्रति यूनिट)
Question 2:
State Ohm’s law. Write the necessary conditions for its validity.
ओम का नियम बताइए तथा इसके प्रयोग की आवश्यक शर्ते लिखिए।
Question 3:
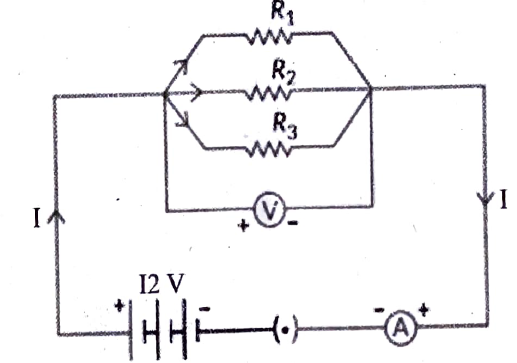
In the cirucuit given below, the resistors R1, R2 and R3 have the values 10Ω, 20Ω and 30Ω respectively, which have been connected to a battery of 12V. Calculate:
(i) The current through each resistor
(ii) The total circuit resistance and
(iii) The total current in the circuit
निम्नलिखित परिपथ में प्रतिरोधक R1 = 10Ω, R2 = 20Ω तथा R3 = 30Ω हैं, जो 12V की बैटरी से जुड़े हैं। गणना कीजिए:
(i) प्रत्येक प्रतिरोधक से प्रवाहित धारा
(ii) कुल परिपथ प्रतिरोध
(iii) परिपथ में प्रवाहित कुल धारा