NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life विज्ञान जीवन की मौलिक इकाई
Page No. 51
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Question 1:
Who discovered cells, and how?
कोशिका की खोज किसने और कैसे की?
Answer
An English Botanist, Robert Hooke discovered cells. In 1665, he used self-designed microscope to observe cells in a cork slice.
सन् 1665 में अंग्रेज वनस्पतिशास्त्री, रॉबर्ट हुक ने कोशिकाओं की खोज की| उन्होंने कार्क की पतली काट में कोशिकाओं का अवलोकन करने के लिए स्वनिर्मित सूक्ष्मदर्शी का प्रयोग किया था|
Question 2:
Why is the cell called the structural and functional unit of life?
कोशिका को जीवन की संरचनात्मक व क्रियात्मक इकाई क्यों कहते हैं?
Answer
Cells are called the structural and functional unit of life because all the living organisms are made up of cells and also all the functions taking place inside the body of organisms are performed by cells.
कोशिका को जीवन की संरचनात्मक व क्रियात्मक इकाई कहते हैं क्योंकि सभी सजीव कोशिका से बने होते हैं तथा उनके शरीर में होने वाली क्रियाओं का संचालन कोशिकाओं द्वारा होता है|
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life विज्ञान जीवन की मौलिक इकाई
Page No. 53
Question 1:
How do substances like CO2 and water move in and out of the cell? Discuss. [Imp.]
CO2 तथा पानी जैसे पदार्थ कोशिका से कैसे अंदर तथा बाहर जाते हैं? इस पर चर्चा करें|
Answer
The substances like CO2 and water move in and out of a cell by diffusion from the region of high concentration to low concentration.
उच्च सांद्रता से निम्न सांद्रता की ओर विसरण द्वारा CO2 तथा पानी जैसे पदार्थ कोशिका से अंदर तथा बाहर जाते हैं| जब कोशिका में CO2 तथा पानी की सांद्रता कोशिका की तुलना में बाह्य वातावरण में उच्च होती है तो ये बाहर निकल जाते हैं और जब बाह्य वातावरण में इनकी सांद्रता कम होती है तो ये कोशिका के अंदर चले जाते हैं|
Question 2:
Why is the plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane? [Imp.]
प्लैज्मा झिल्ली को वर्णात्मक पारगम्य झिल्ली क्यों कहते हैं?
Answer
Plasma membrane called a selectively permeable membrane because it regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. This means that the plasma membrane allows the entry of only some substances and prevents the movement of some other materials.
प्लैज्मा झिल्ली को वर्णात्मक पारगम्य झिल्ली कहते हैं क्योंकि यह कोशिका के घटकों को बाहरी पर्यावरण से अलग करती है| इसका अर्थ है कि यह कुछ पदार्थों को अंदर अथवा बाहर आने-जाने देती है| यह अन्य पदार्थों की गति को भी रोकती है|
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life विज्ञान जीवन की मौलिक इकाई
Page No. 55
Question 1:
Fill in the gaps in the following table illustrating differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
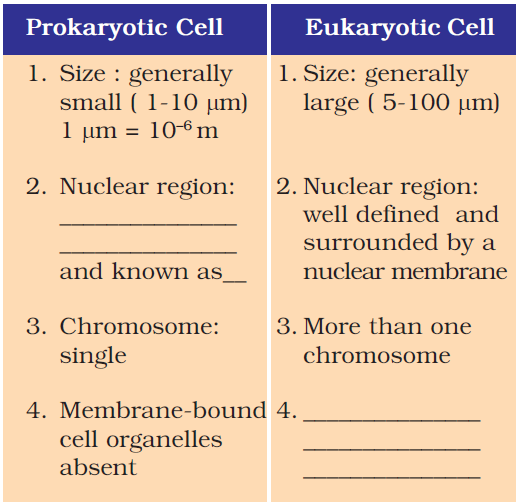
क्या अब आप निम्नलिखित तालिका में दिए गए रिक्त स्थानों को भर सकते हैं, जिससे कि प्रोकैरियोटी तथा यूकैरियोटी कोशिकाओं में अंतर स्पष्ट हो सके:
Answer
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
| 1. Size: Generally small (1-10 μm) 1 μm = 10 -6 m 2. The nuclear region is poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane and is known as the nucleoid. 3. There is a single chromosome. 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles absent. | 1. Size: Generally large (5-100 μm) 2. Nuclear region: well-defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane. 3. There is more than one chromosome. 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles present. |
| प्रोकैरियोटी कोशिका | यूकैरियोटी कोशिका |
| आकार प्रायः छोटा (1-10 µm) 1µm = 10-6 m | आकार प्रायः बड़ा (5-100 µm) |
| केंद्रकीय क्षेत्र : केंद्रकीय झिल्ली की अनुपस्थिति में अस्पष्ट होते हैं| | केंद्रकीय क्षेत्र : सुस्पष्ट जो चारों ओर से केंद्रकीय झिल्ली से घिरा होता है| |
| क्रोमोसोम : एक | क्रोमोसोम : एक से अधिक |
| झिल्ली युक्त कोशिका अंगक अनुपस्थित | झिल्ली युक्त कोशिका अंगक जैसे- प्लैस्टिड, माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया आदि उपस्थित होते हैं| |
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life विज्ञान जीवन की मौलिक इकाई
Page No. 57
Question 1:
Can you name the two organelles we have studied that contain their own genetic material?
क्या आप दो ऐसे अंगकों का नाम बता सकते हैं जिनमें अपना आनुवांशिक पदार्थ होता है?
Answer
Mitochondria and plastids
प्लैस्टिड तथा माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया|
Question 2:
If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence, what will happen? [Imp.]
यदि किसी कोशिका का संगठन किसी भौतिक अथवा रासायनिक प्रभाव के कारण नष्ट हो जाता है, तो क्या होगा?
Answer
If the organisation of a cell is destroyed due to some physical or chemical influence then cell will not be able to perform the basic functions like respiration, nutrition, excretion etc. This may stop all the life activities and may result in its death.
यदि किसी कोशिका का संगठन किसी भौतिक अथवा रासायनिक प्रभाव के कारण नष्ट हो जाता है, तो श्वसन, पोषण, उत्सर्जन आदि जैसे विशिष्ट कार्यों को पूरा करने में कोशिका सक्षम नहीं रहते| इससे जीवन की गतिविधियाँ रूक सकती है तथा मृत्यु भी हो सकती है|
Question 3:
Why are lysosomes known as suicide bags? [Imp.]
लाइसोसोम को आत्मघाती थैली क्यों कहते हैं?
Answer
Lysosomes are called suicide bags because in case of disturbance of their cellular metabolism they digest their own cell by releasing own enzymes.
कोशिकीय चयापचय में व्यवधान के कारण जब कोशिका क्षतिग्रस्त या मृत हो जाती है, तो लाइसोसोम फट जाते हैं और एंजाइम अपनी ही कोशिकाओं को पाचित करते हैं, इसलिए इन्हें कोशिका की आत्मघाती थैली कहते हैं|
Question 4:
Where are proteins synthesised inside the cell?
कोशिका के अंदर प्रोटीन का संश्लेषण कहाँ होता है?
Answer
The proteins are synthesized in the Ribosome inside the cell.
कोशिका के अंदर प्रोटीन का संश्लेषण राइबोसोम में होता है|
NCERT Solutions of Class 9 Science Ch-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life विज्ञान जीवन की मौलिक इकाई
Page No. 59
Exercise
Question 1:
Make a comparison and write down ways in which plant cells are different from animal cells.
पादप कोशिकाओं तथा जंतु कोशिकाओं में तुलना करो|
Answer

| पादप कोशिका | जंतु कोशिका |
| इनमें सेल्यूलोज से बनी कोशिका भित्ति होती है| | इनमें कोशिका भित्ति नहीं होती है| |
| इनमें क्लोरोप्लास्ट पाया जाता है| | इनमें क्लोरोप्लास्ट नहीं होता है| |
| इनमें क्रोमोसोम नहीं होता है| | इनमें क्रोमोसोम होते हैं| |
| पादप कोशिकाओं में रसधानियाँ बड़ी होती हैं| | जंतु कोशिकाओं में रसधानियाँ छोटी होती हैं| |
| लाइसोसोम की संख्या बहुत कम या अनुपस्थित होते हैं| | लाइसोसोम की संख्या बहुत अधिक होती है| |
Question 2:
How is a prokaryotic cell different from a eukaryotic cell?
प्रोकैरियोटी कोशिकाएँ युकैरियोटी कोशिकाओं से किस प्रकार से किस प्रकार भिन्न होती हैं?
Answer
| Prokaryotic Cell | Eukaryotic Cell |
| 1. Size: Generally small (1-10 μm) 1 μm = 10 -6 m 2. The nuclear region is poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane and is known as the nucleoid. 3. There is a single chromosome. 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles absent. | 1. Size: Generally large (5-100 μm) 2. Nuclear region: well-defined and surrounded by a nuclear membrane. 3. There is more than one chromosome. 4. Membrane-bound cell organelles present. |
| प्रोकैरियोटी कोशिका | यूकैरियोटी कोशिका |
| आकार प्रायः छोटा (1-10 µm) 1µm = 10-6 m | आकार प्रायः बड़ा (5-100 µm) |
| केंद्रकीय क्षेत्र : केंद्रकीय झिल्ली की अनुपस्थिति में अस्पष्ट होते हैं| | केंद्रकीय क्षेत्र : सुस्पष्ट जो चारों ओर से केंद्रकीय झिल्ली से घिरा होता है| |
| क्रोमोसोम : एक | क्रोमोसोम : एक से अधिक |
| झिल्ली युक्त कोशिका अंगक अनुपस्थित | झिल्ली युक्त कोशिका अंगक जैसे- प्लैस्टिड, माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया आदि उपस्थित होते हैं| |
Question 3:
What would happen if the plasma membrane ruptures or breaks down?
यदि प्लैज्मा झिल्ली फट जाए अथवा टूट जाए तो क्या होगा?
Answer
If the plasma membrane ruptures or breakdown then the cell will not be able to exchange material from its surrounding by diffusion or osmosis. Thereafter the protoplasmic material will be disappeared and the cell will die.
यदि प्लैज्मा झिल्ली फट जाए अथवा टूट जाए तो कोशिका परासरण अथवा विसरण द्वारा बाह्य पदार्थों का आदान-प्रदान करने में सक्षम नहीं रहेगा| इसके बाद जीवद्रव्यक पदार्थ उपस्थित नहीं रहेगा तथा कोशिका मृत हो जाएगी|
Question 4:
What would happen to the life of a cell if there was no Golgi apparatus?
यदि गॉल्जी उपकरण न हो तो कोशिका के जीवन में क्या होगा?
Answer
Golgi apparatus has the function of storage modification and packaging of the products. If there is no Golgi apparatus then the packaging and transporting of materials synthesized by cell will not happen.
गॉल्जी उपकरण में अंतर्द्रव्यी जालिका में संश्लेषित पदार्थ पैक किए जाते हैं और उन्हें कोशिका के बाहर तथा अंदर विभिन्न क्षेत्रों में भेज दिया जाता है| यदि गॉल्जी उपकरण न हो तो कोशिका द्वारा संश्लेषित पदार्थों का संचयन, रूपांतरण तथा पैकेजिंग नहीं होगा|
Question 5:
Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell? Why?
कोशिका का कौन-सा अंगक बिजलीघर है? और क्यों?
Answer
Mitochondria is known as powerhouse of the cell because it releases the energy required for different activities of life.
माइटोकॉन्ड्रिया को कोशिका का बिजलीघर कहा जाता है क्योंकि जीवन के लिए आवश्यक विभिन्न रासायनिक क्रियाओं को करने के लिए यह ATP (ऐडिनोसिन ट्राइफॉस्फेट) के रूप में ऊर्जा प्रदान करते हैं|
Class 9 Science Ch-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Question 6:
Where do the lipids and proteins constituting the cell membrane get synthesised?
कोशिका झिल्ली को बनाने वाले लिपिड तथा प्रोटीन का संश्लेषण कहाँ होता है?
Answer
Lipids are synthesized in Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) and the proteins are synthesized in rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER).
लिपिड का संश्लेषण चिकनी अंतर्द्रव्यी जालिका (SER) तथा प्रोटीन का संश्लेषण खुरदरी अंतर्द्रव्यी जालिका (RER) में होता है|
Question 7:
How does an Amoeba obtain its food?
अमीबा अपना भोजन कैसे प्राप्त करता है?
Answer
Amoeba take it’s food by the cell membrane which forms the food vacuole.
अमीबा भोजन कणों को कोशिका सतह पर बने अस्थायी प्रवर्ध (कूटपादों) से घेर लेता है, फिर कूटपादों के एक दुसरे से मिल जाने से भोजन का कुछ कण कुछ तरल के साथ खाद्य रसधानी के रूप में कोशारस में पहुँच जाता है| अपाच्य भाग चलनक्रिया के बीच क्रमशः शरीर के पिछले भाग में पहुँचता है और फिर उसका परित्याग हो जाता है|
Question 8:
What is osmosis?
परासरण क्या है?
Answer
Osmosis is the process in which water molecules moves from the region of high concentration to a region of low concentration through a semi permeable membrane.
जल के अणुओं की गति जब वर्णात्मक पारगम्य झिल्ली द्वारा उच्च जल की सांद्रता से निम्न जल की सांद्रता की ओर जाते हैं तो उसे परासरण कहते हैं|
Class 9 Science Ch-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Question 9:
Carry out the following osmosis experiment:
Take four peeled potato halves and scoos each one out to make potato cups. One of these potato cups should be made from a boiled potato. Put each potato cup in a trough containing water. Now,
(a) Keep cup A empty
(b) Put one teaspoon sugar in cup B
(c) Put one teaspoon salt in cup C
(d) Put one teaspoon sugar in the boiled potato cup D.
Keep these for two hours. Then observe the four potato cups and answer the following:
(i) Explain why water gathers in the hollowed portion of B and C.
(ii) Why is potato A necessary for this experiment?
(iii) Explain why water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D.
निम्नलिखित परासरण प्रयोग करें :
छिले हुए आधे-आधे आलू के चार टुकड़े लो, इन चारों को खोखला करो जिससे कि आलू के कप बन जाएँ| इनमें से एक कप को उबले आलू में बनाना है| आलू के प्रत्येक कप को जल वाले बर्तन में रखो| अब
(a) कप ‘A’ को खाली रखो,
(b) कप ‘B’ में एक चम्मच चीनी डालो,
(c) कप ‘C’ में एक चम्मच नमक डालो तथा
(d) उबले आलू से बनाए गए कप ‘D’ में एक चम्मच चीनी डालो|
आलू के इन चारों कपों को दो घंटे तक रखने के पश्चात् उनका अवलोकन करो तथा निम्न प्रश्नों का उत्तर दो :
(i) ‘B’ तथा ‘C’ के खाली भाग में जल क्यों एकत्र हो गया? इसका वर्णन करो|
(ii) ‘A’ आलू इस प्रयोग के लिए क्यों महत्वपूर्ण है?
(iii) ‘A’ तथा ‘D’ आलू के खाली भाग में जल एकत्र क्यों नहीं हुआ? इसका वर्णन करो|
Answer
(i) Water gathers in B and C because in both the situations there is difference in the concentration of water in the trough and water in the cup of Potato. Hence, osmosis takes place as the potato cells act as a semi-permeable membrane.
(ii) Potato A is necessary for this experiment for comparison, it acts as a control.
(iii) Water does not gather in the hollowed out portions of A and D. As cup of A does not have change in the concentration for water to flow. For osmosis to occur one of the concentration should be higher than the other.
In cup D, the cells are dead and hence the semi-permeable membrane does not exists for the flow of water and no osmosis takes place.
(i) ‘B’ तथा ‘C’ के खाली भाग में जल एकत्र हो गया क्योंकि परासरण के कारण जल आलू में जमा हो जाता है| चूँकि कोशिका के आस-पास के माध्यम में कोशिका की तुलना में उच्च जल की सांद्रता मौजूद है, इसलिए जल परासरण विधि द्वारा कोशिका के अंदर चला जाएगा| इस प्रकार आलू कप के खाली भाग में जल एकत्र हो जाता है|
(ii) ‘A’ आलू इस प्रयोग में नियंत्रण व्यवस्था के रूप में कार्य करता है| ‘A’ आलू के खाली भाग में जल एकत्र नही होता है|
(iii) ‘A’ आलू के खाली भाग में जल एकत्र नहीं हुआ क्योंकि आलू का कप ‘A’ खाली है| ‘D’ आलू के खाली भाग में भी जल एकत्र नहीं हुआ क्योंकि इसमें उबला आलू प्रयोग किया गया है| उबालने से कोशिका झिल्ली में उपस्थित प्रोटीन विकृत हो जाता है और कोशिका झिल्ली नष्ट हो जाती है| परासरण के लिए वर्णात्मक पारगम्य झिल्ली की आवश्यकता होती है, जो कि इस स्थिति में नष्ट हो चुका है| इसलिए परासरण की क्रिया नहीं होती| इस प्रकार उबले आलू के खाली भाग में जल एकत्र नहीं होता है|
Class 9 Science Ch-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Question 10:
Which type of cell division is required for growth and repair of body and which type is involved in formation of gametes?
Answer
Mitosis is required for growth and repair of body and meiosis is involved in the formation of gametes.
Class 9 Science Ch-5 The Fundamental Unit of Life

