NCERT Solution for Class 10 Civics Chapter 3 Gender, Religion and Caste जाति, धर्म और लैंगिक मसले
Important Questions for Class 10 Civics Chapter 3
Thank you for reading this post, don't forget to subscribe!Exercises
Question 1:
Mention different aspects of life in which women are discriminated or disadvantaged in India.
जीवन के उन विभिन्न पहलुओं का जिक्र करें जिनमें भारत में महिलाओं के साथ भेदभाव होता है या वो कमजोर स्थिति में होती है?
Answer
In India, women are discriminated and disadvantaged in the following ways:
(1) They are not provided adequate education. Thus, the literacy rate among women is just 54%.
(2) Most of the labour done by them is unpaid. Where they are paid for their work, they receive lesser wages than men.
(3) Due to the preference for the boy child, female foeticide is practiced in many parts of the country.
भारत में महिलाओं को निम्न तरीकों से भेदभाव किया जाता है:
(1) उन्हें पर्याप्त शिक्षा नहीं दी जाती है। जिस कारण महिलाओं में साक्षरता केवल 54% है।
(2) उनके द्वारा किया गया अधिकांश श्रम अवैतनिक है। जहां वे काम करती है उन्हें पुरुषों की तुलना में कम वेतन मिलता है।
(3) सिर्फ लड़के की चाह के कारण देश के कई हिस्सों में कन्या भ्रूण हत्या का प्रचलन है।
Question 2:
State different forms of communal politics with one example each.
विभिन्न तरह की सांप्रदायिक राजनीति का ब्यौरा दे और सब के साथ एक-एक उदारहण भी दें?
Answer
Communal politics takes several dangerous forms:
(1) Everyday Beliefs and Prejudices – It begins with ordinary people holding biased views against other religions. Example: Considering one’s religion superior and discriminating against others.
(2) Political Mobilisation – Religious leaders and political parties appeal to people based on religion.
Example: Using religious slogans or festivals during elections to gather votes.
(3) Communal Violence – It is the most extreme form where religion-based hatred leads to violence.
Example: The Gujarat riots of 2002.
सांप्रदायिक राजनीति के कई रूप होते हैं:
(1) रोजमर्रा की मान्यताएं और पूर्वाग्रह – इसमें लोग अपनी ही धर्म को श्रेष्ठ मानते हैं और दूसरों को नीचा समझते हैं।
उदाहरण: यह मानना कि केवल एक धर्म ही सच्चा है और बाकी गलत हैं।
(2) राजनीतिक लामबंदी – राजनीतिक दल धर्म के नाम पर लोगों को एकजुट करते हैं।
उदाहरण: चुनावों में धार्मिक नारे लगाना या धार्मिक भावनाओं को भड़काना।
(3) सांप्रदायिक हिंसा – जब धार्मिक मतभेद हिंसक टकराव में बदल जाते हैं।
उदाहरण: 2002 का गुजरात दंगा।
Question 3:
State how caste inequalities are still continuing in India.
बताइए की भारत में किस तरह अभी भी जातिगत असमानताएँ जारी हैं।
Answer
Caste has not disappeared from contemporary India.
(1) Even now most people marry within their own caste or tribe.
(2) Untouchability has not ended completely despite constitutional prohibition.
(3) Effects of centuries of advantages and disadvantages continue to be felt today, e.g., Caste continues to be closely linked to economic status.
समकालीन भारत से जाति व्यवस्था खत्म नहीं हुई है।
(1) अब भी ज्यादातर लोग अपनी जाति या कबीले के अंदर ही शादी करते हैं।
(2) छुआछूत को संवैधानिक किये जाने के बावजूद भी यह पूरी तरह से समाप्त नहीं हुई है।
(3) सदियों पुराने चलन के प्रभावों को आज भी महसूस किया जाता है, जैसे कि जाति को आर्थिक स्थिति का पैमाना माना जाता है।
Question 4:
State two reasons to say that caste alone cannot determine election results in India.
दो कारण बताए कि क्यों सिर्फ जाति के आधार पर भारत में चुनाव के परिणाम तय नहीं हो सकते?
Answer
Caste alone cannot determine election results in India because:
(1) No parliamentary constituency has a clear majority of one single caste.
(2) No party wins all the votes of a particular caste.
अकेले जाति भारत में चुनाव परिणाम निर्धारित नहीं कर सकता क्योंकि:
(1) कोई भी संसदीय क्षेत्र ऐसा नहीं है जहाँ एक ही जाति का स्पष्ट बहुमत हो।
(2) कोई भी पार्टी किसी विशेष जाति के सभी वोट हासिल नहीं करती है।
Question 5:
What is the status of women’s representation in India’s legislative bodies?
भारत विधायिकाओं में महिलाओं के प्रतिनिधित्व की स्थिति क्या है?
Answer
When it comes to representation of women in legislative bodies, India is among the bottom group of nations in the world. Women’s representation has always been less than 10% in Lok Sabha and 5% in the State Assemblies.
On the other hand, the situation is different in the case of local government bodies. As one-third of seats in local government bodies (panchayats and municipalities) is reserved for women, there are more than 10 lakh elected women representatives in rural and urban local bodies.
जब विधायिकाओं में महिलाओं के प्रतिनिधित्व की बात आती है, तो भारत का स्थान दुनिया के देशों में सबसे नीचे है। महिलाओं का प्रतिनिधित्व हमेशा लोकसभा में 10% से कम और राज्य विधानसभाओं में 5% रहा है। दूसरी तरफ स्थानीय सरकारी निकायों के मामले में स्थिति अलग है। चूंकि स्थानीय सरकारी निकायों (पंचायतों और नगर पालिकाओं) में महिलाओं के लिए एक तिहाई सीटें आरक्षित हैं, ग्रामीण और शहरी स्थानीय निकायों में 10 लाख से अधिक निर्वाचित प्रतिनिधि महिलाऐं हैं।
Question 6:
Mention any two constitutional provisions that make India a secular state.
किन्हीं दो प्रावधानों का जिक्र करें जो भारत को एक धर्मनिरपेक्ष देश बनाते हैं?
Answer
Two constitutional provisions that make India a secular state are:
(1) Freedom to practice, profess and propagate the religion of one’s choice.
(2) The Constitution prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion.
भारत को धर्मनिरपेक्ष देश बनाने वाले दो संवैधानिक प्रावधान निम्न हैं:
(1) किसी भी धर्म का प्रचार करने, अभ्यास करने और अपनाने की स्वतंत्रता है।
(2) संविधान धर्म के आधार पर भेदभाव पर रोक लगाता है।
Question 7:
When we speak of gender divisions, we usually refer to:
(a) Biological difference between men and women
(b) Unequal roles assigned by the society to men and women
(c) Unequal child sex ratio
(d) Absence of voting rights for women in democracies
जब हम लिंग विभाजन की बात करते हैं तो हमारा अभिप्राय होता है:
(क) पुरुषों और महिलाओं के बीच जैविक अंतर
(ख) समाज द्वारा स्त्री और पुरुष को दी गई असमान भूमिकाएँ
(ग) बालक और बालिकाओं की संख्या का अनुपात
(घ) लोकतांत्रिक व्यवस्थाओं में महिलाओं को मतदान का अधिकार न मिलना
Answer
(b) Unequal roles assigned by the society to men and women
(ख) समाज द्वारा स्त्री और पुरुष को दी गई असमान भूमिकाएँ
Question 8:
In India seats are reserved for women in
(a) Lok Sabha
(b) State Legislative Assemblies
(c) Cabinets
(d) Panchayati Raj bodies
भारत में महिलाओं के लिए आरक्षण की व्यवस्था है:
(क) लोकसभा
(ख) विधानसभा
(ग) मंत्रिमंडल
(घ) पंचायतीराज संस्थाएँ
Answer
(d) Panchayati Raj bodies
(घ) पंचायतीराज संस्थाएँ
Question 9:
Consider the following statements on the meaning of communal politics. Communal politics is based on the belief that:
A. One religion is superior to that of others.
B. People belonging to different religions can live together happily as equal citizens.
C. Followers of a particular religion constitute one community.
D. State power cannot be used to establish the domination of one religious group over others.
Which of the statements is/are correct?
(a) A, B, C and D
(b) A, B and D
(c) A and C
(d) B and D
सांप्रदायिक राजनीति के अर्थ संबंधी निम्नलिखित कथनों पर विचार करें। सांप्रदायिक राजनीति इस धारणा पर आधारित है कि:
(क) एक धर्म दूसरों से बेहतर है
(ख) विभिन्न धर्मों के लोग समान नागरिक के रूप में खुशी खुशी साथ रह सकते हैं
(ग) एक धर्म के अनुयायी एक समुदाय बनाते हैं
(घ) एक धार्मिक समूह का प्रभुत्व बाकी सभी धर्मों पर कायम करने में शासन की शक्ति का उपयोग नहीं किया जा सकता है
कौन सा कथन सही है / हैं?
(क) क, ख, ग और घ
(ख) क, ख और घ
(ग) क और ग
(घ) ख और घ
Answer
(c) A and C
Question 10:
Which among the following statements about India’s Constitution is wrong? It
(a) prohibits discrimination on grounds of religion
(b) gives official status to one religion
(c) provides to all individuals freedom to profess any religion
(d) ensures equality of citizens within religious communities
भारत के संविधान के बारे में निम्नलिखित में से कौन सा कथन गलत है?
(क) धर्म के आधार पर भेदभाव की मनाही करता है।
(ख) यह एक धर्म को राजकीय धर्म बताता है।
(ग) सभी व्यक्तियों को कोई भी धर्म को स्वीकार करने की आजादी देता है।
(घ) किसी धार्मिक समुदाय में सभी नागरिकों को बराबरी का अधिकार देता है।
Answer
(b) gives official status to one religion
(ख) यह एक धर्म को राजकीय धर्म बताता है।
Question 11:
Social divisions based on ______________ are peculiar to India.
___________ पर आधारित सामाजिक विभाजन सिर्फ भारत में ही है।
Answer
caste
जाति
Question 12:
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the Lists:
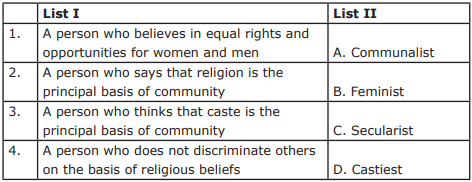
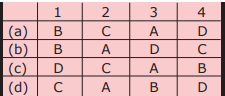
सूची I और सूची II का मिलान करें और नीचे दिए गए कोड के आधार पर सही उत्तर चुनें:
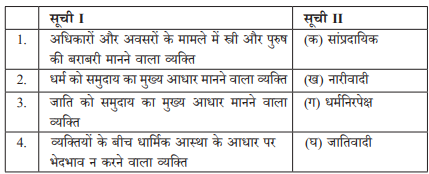
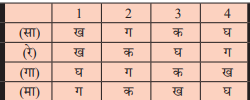
Answer
(b)
NCERT Solution for Class 10 Civics Ch-3 Gender, Religion and Caste जाति, धर्म और लैंगिक मसले

